Squeaky Science: Researchers Uncover Genetic Twist Behind Unusual Mouse Vocalizations
Science
2025-02-18 10:02:01Content
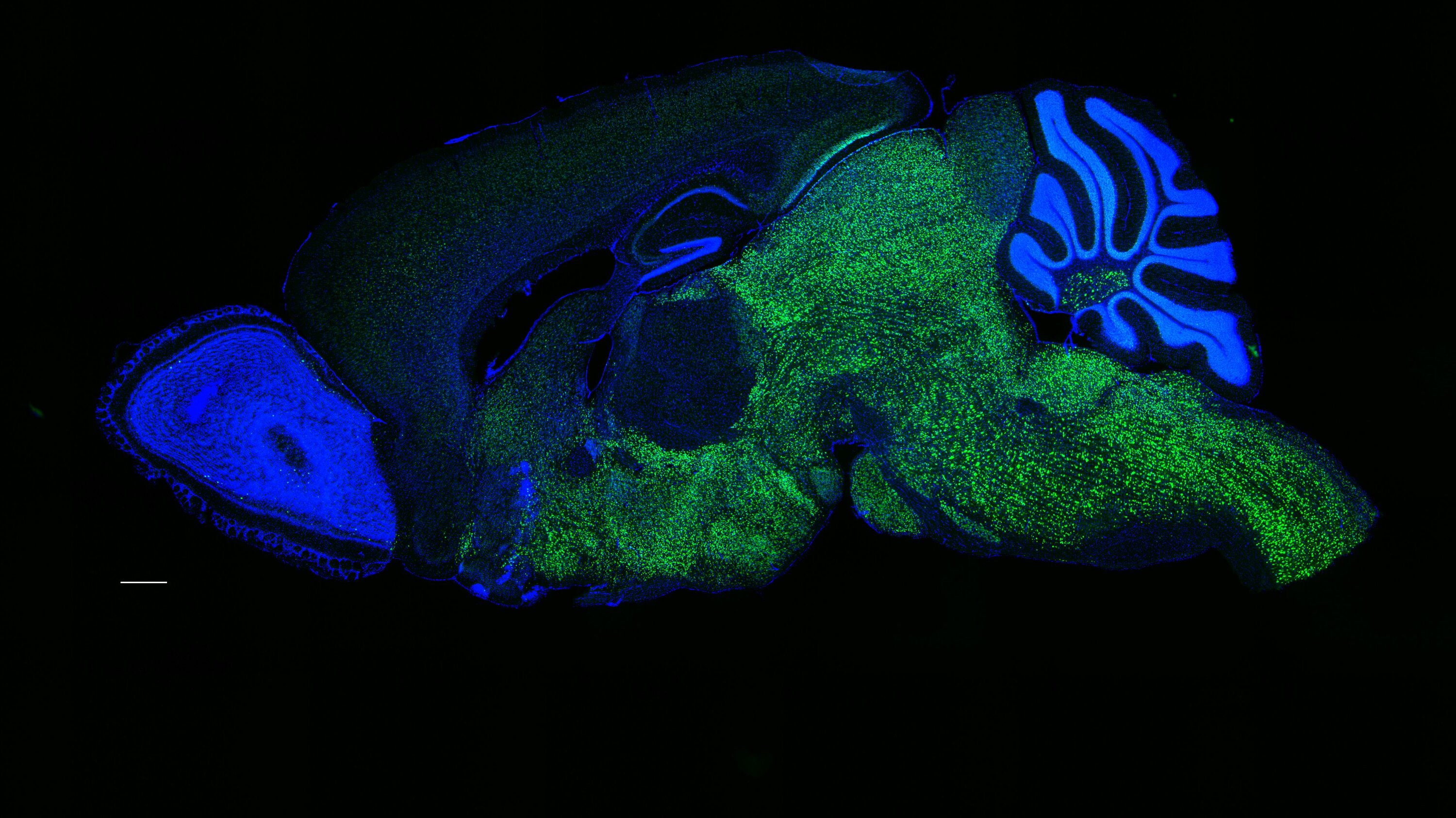
Scientists have uncovered a fascinating genetic breakthrough that could shed light on one of humanity's most remarkable capabilities: language. Researchers have discovered that the NOVA1 gene may have played a crucial role in the evolutionary development of human communication.
This groundbreaking finding suggests that a single genetic variation might have been instrumental in setting humans apart from other species, potentially explaining the complex linguistic abilities that define our species. The NOVA1 gene appears to have been a critical molecular switch in our evolutionary journey, helping to shape the neural pathways that enable sophisticated verbal communication.
While previous research has explored the origins of human language, this study offers a compelling new perspective on the genetic mechanisms that may have contributed to our unique communicative skills. By examining the intricate genetic landscape of human development, scientists are gradually unraveling the molecular mysteries behind what makes human communication so extraordinary.
The research highlights the remarkable complexity of human evolution and underscores how subtle genetic changes can have profound implications for our species' cognitive capabilities. As scientists continue to explore the genetic foundations of language, we move closer to understanding the remarkable journey that has shaped human communication.
Decoding the Linguistic Leap: How NOVA1 Gene Revolutionizes Human Communication
In the intricate landscape of human evolution, few discoveries have been as groundbreaking as the recent insights into our linguistic capabilities. Scientists have long pondered the mysterious origins of human language, that remarkable ability which distinguishes us from other species and has been the cornerstone of our unprecedented cultural and technological advancement.Unraveling the Genetic Blueprint of Human Expression
The Genetic Foundations of Communication
The human capacity for complex communication represents a quantum leap in biological development. Researchers have discovered that the NOVA1 gene plays a pivotal role in this extraordinary evolutionary journey. Unlike previous understanding, this genetic marker appears to be far more than a simple biological instruction set. It represents a sophisticated neural programming mechanism that fundamentally transformed how human brains process and generate language. Neurological studies reveal that NOVA1 influences neural connectivity in ways previously unimagined. The gene's unique mutation appears to have dramatically enhanced synaptic plasticity, creating intricate neural networks that enable more nuanced and complex communication patterns. This genetic variation potentially explains why humans can articulate abstract concepts, engage in sophisticated reasoning, and develop intricate linguistic structures that no other species can replicate.Evolutionary Implications of Linguistic Complexity
The emergence of advanced linguistic capabilities represents more than a mere biological adaptation. It signifies a profound cognitive revolution that reshaped human social interactions, knowledge transmission, and collective intelligence. By enabling more sophisticated communication, the NOVA1 gene mutation likely accelerated cultural evolution, allowing our ancestors to share complex ideas, coordinate sophisticated hunting strategies, and develop increasingly intricate social structures. Comparative genetic research demonstrates that this particular gene mutation is uniquely human. While primates and other advanced mammals possess communication systems, none approach the complexity and flexibility of human language. The NOVA1 gene appears to be the critical differentiator, providing neural architecture that supports abstract thinking, metaphorical reasoning, and recursive language patterns.Neurological Mechanisms of Language Development
Cutting-edge neuroimaging techniques have provided unprecedented insights into how the NOVA1 gene influences brain development. Researchers have observed that this genetic marker significantly impacts neural connectivity, particularly in regions associated with language processing. The gene seems to create more extensive and efficient neural networks, allowing for faster and more complex information transmission. This enhanced neural connectivity explains why humans can learn multiple languages, understand complex grammatical structures, and rapidly adapt linguistic skills. The NOVA1 gene doesn't just enable communication; it creates a dynamic, flexible neural environment that continuously evolves and refines linguistic capabilities throughout an individual's lifetime.Broader Scientific and Philosophical Implications
The discovery of NOVA1's role in language evolution transcends biological research. It challenges fundamental philosophical questions about consciousness, communication, and what distinguishes human cognitive capabilities. By understanding the genetic underpinnings of our linguistic abilities, scientists are gaining profound insights into the very nature of human intelligence and social interaction. Moreover, this research opens exciting possibilities for understanding language disorders, cognitive development, and potential therapeutic interventions. The intricate relationship between genetics and communication provides a new lens through which we can explore human potential and neurological diversity.Future Research and Potential Applications
As scientific methodologies become increasingly sophisticated, researchers anticipate further breakthroughs in understanding the NOVA1 gene's complex mechanisms. Potential applications range from developing targeted therapies for language-related disorders to exploring enhanced communication strategies in artificial intelligence and human-machine interactions. The ongoing investigation into this remarkable genetic marker promises to unveil even more extraordinary insights into human cognitive evolution, challenging our understanding of genetics, neuroscience, and the fundamental nature of human communication.RELATED NEWS
Science

AI Revolution: How Machine Learning is Transforming Peer Review in Scientific Research
2025-03-29 01:39:00
Science

The Taxpayer's Dilemma: Should Science Research Really Be Publicly Funded?
2025-04-25 21:19:00
Science

Cosmic Threat Looms: Massive 'City-Killer' Asteroid Inches Closer to Earth's Doorstep
2025-02-18 18:06:57





