Ecological Lifeline: Five African Nations Unite to Rescue Lake Tanganyika's Fragile Ecosystem
Environment
2025-02-26 00:00:00Content
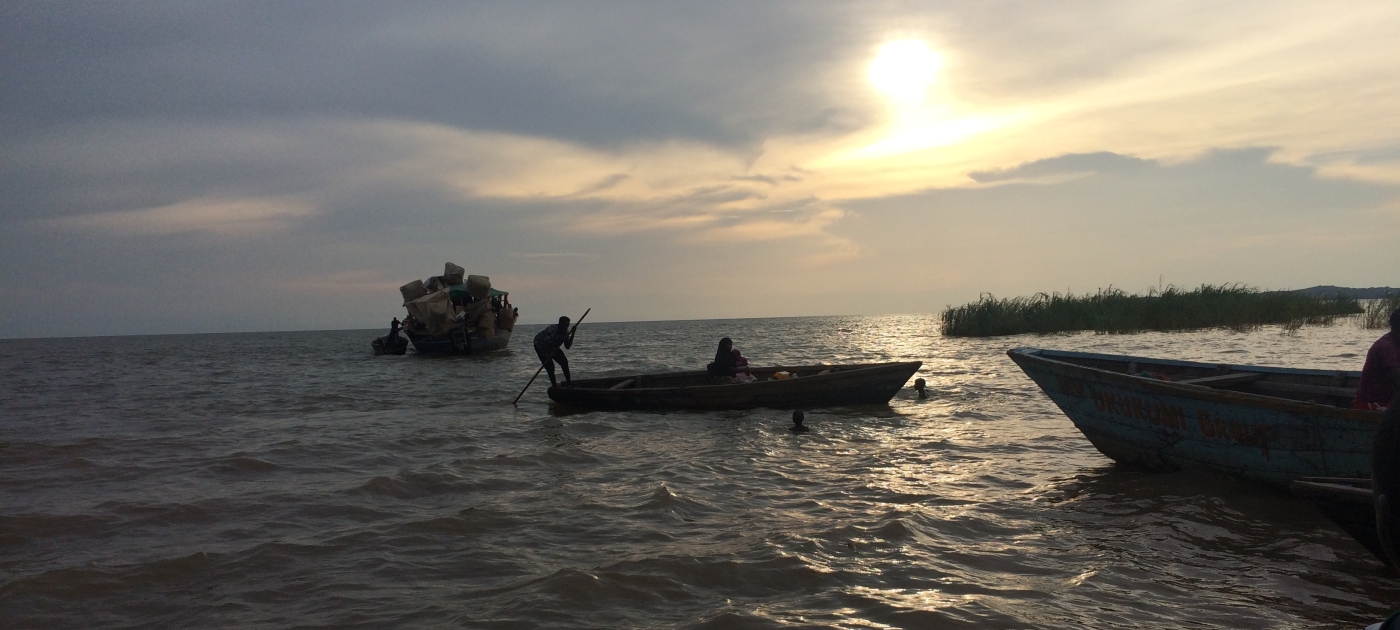

In a groundbreaking collaborative effort, four East African nations have embarked on an ambitious five-year initiative to protect and restore critical transboundary ecosystems. Burundi, the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), Tanzania, and Zambia have joined forces to tackle pressing environmental challenges that threaten the region's rich biodiversity and natural resources.
The ambitious $14.5 million project, generously funded by the Global Environment Facility (GEF), represents a comprehensive approach to environmental conservation. Its multifaceted strategy focuses on several key areas: revitalizing sustainable fisheries, preserving unique biodiversity, rehabilitating degraded landscapes, and strengthening cross-border environmental cooperation.
As global concerns about biodiversity loss and ecosystem degradation continue to mount, this innovative project stands as a beacon of hope. By bringing together four nations with interconnected ecological systems, the initiative aims to create a holistic and coordinated approach to environmental protection.
The project will not only address immediate environmental challenges but also lay the groundwork for long-term sustainable development in the region. Through collaborative research, shared conservation strategies, and joint management efforts, these nations are setting a powerful example of international environmental stewardship.
Experts hope this groundbreaking initiative will serve as a model for transboundary environmental cooperation, demonstrating how nations can work together to protect our planet's most precious natural resources.
Ecological Renaissance: Four Nations Unite to Rescue Lake Tanganyika's Fragile Ecosystem
In the heart of Africa, a groundbreaking environmental initiative is taking shape, promising to transform the ecological landscape of one of the continent's most critical water bodies. Four nations have embarked on an ambitious journey to address the mounting challenges threatening the delicate balance of Lake Tanganyika's biodiversity and sustainable development.Urgent Action: Preserving Africa's Liquid Lifeline
The Collaborative Environmental Intervention
Lake Tanganyika represents more than just a geographical landmark; it is a complex ecosystem that sustains millions of lives across multiple national boundaries. The collaborative effort between Burundi, Democratic Republic of Congo, Tanzania, and Zambia marks a pivotal moment in transboundary environmental conservation. This unprecedented partnership demonstrates a sophisticated approach to addressing ecological challenges that transcend traditional political limitations. The project, meticulously designed with a substantial investment of USD 14.5 million from the Global Environment Facility (GEF), represents a holistic strategy to combat environmental degradation. By integrating sustainable fisheries management, biodiversity conservation, and landscape restoration, the initiative aims to create a comprehensive ecological intervention that balances human needs with environmental preservation.Ecological Complexity and Biodiversity Challenges
The lake's ecosystem is extraordinarily complex, hosting an incredible diversity of aquatic life that has evolved over millions of years. Recent scientific assessments have highlighted the increasing vulnerability of this unique environment, with climate change, overfishing, and habitat destruction posing significant threats to its delicate ecological balance. Researchers have documented alarming trends of species decline and habitat fragmentation, underscoring the critical nature of this multinational conservation effort. The project's approach goes beyond traditional conservation methods, incorporating advanced ecological monitoring, community engagement, and sustainable development strategies.Sustainable Fisheries and Community Empowerment
Central to the project's success is a nuanced approach to sustainable fisheries management. By implementing innovative fishing practices and providing alternative economic opportunities, the initiative seeks to reduce ecological pressure while simultaneously supporting local communities. Local fishermen will receive comprehensive training in sustainable fishing techniques, ecosystem management, and alternative livelihood strategies. This multifaceted approach ensures that conservation efforts are not perceived as restrictive but as opportunities for economic and environmental transformation.Technological Innovation in Environmental Restoration
The project leverages cutting-edge technological solutions to address landscape degradation and biodiversity loss. Advanced satellite monitoring, genetic research, and ecological modeling will provide unprecedented insights into the lake's complex ecosystem. Innovative restoration techniques, including targeted reforestation, watershed management, and habitat reconstruction, will be deployed to rehabilitate degraded landscapes. These interventions represent a sophisticated approach to ecological restoration that goes beyond traditional conservation methodologies.Transboundary Cooperation: A Model for Global Environmental Management
The Lake Tanganyika initiative serves as a potential blueprint for international environmental cooperation. By transcending political boundaries and creating a unified approach to ecological challenges, these four nations are demonstrating the potential for collaborative environmental management. Diplomatic channels have been carefully navigated to ensure seamless cooperation, with each nation contributing unique expertise and resources. This approach not only addresses immediate ecological concerns but also establishes a framework for future transboundary environmental initiatives.Long-term Impact and Global Significance
While the immediate focus is on Lake Tanganyika, the broader implications of this project extend far beyond regional boundaries. The comprehensive approach to ecosystem management, community engagement, and sustainable development offers valuable insights for global environmental conservation efforts. International environmental organizations are closely monitoring this initiative, recognizing its potential to serve as a transformative model for addressing complex ecological challenges in developing regions.RELATED NEWS
Environment

Rare Naked Turtle Mystery: DLNR Seeks Public Help to Solve Ewa Beach Shell Enigma
2025-03-28 20:39:00
Environment

EPA Water Rules Triumph: Supreme Court Backs San Francisco in Landmark Decision
2025-03-04 15:59:09
Environment

Hanford's High-Stakes Media Purge: 11,000 Pounds of Secrets Destroyed to Safeguard National Security
2025-02-21 00:23:00