Silent Invader: How a Common Parasite Could Dramatically Increase Your Cervical Cancer Risk
Science
2025-04-23 19:35:00Content
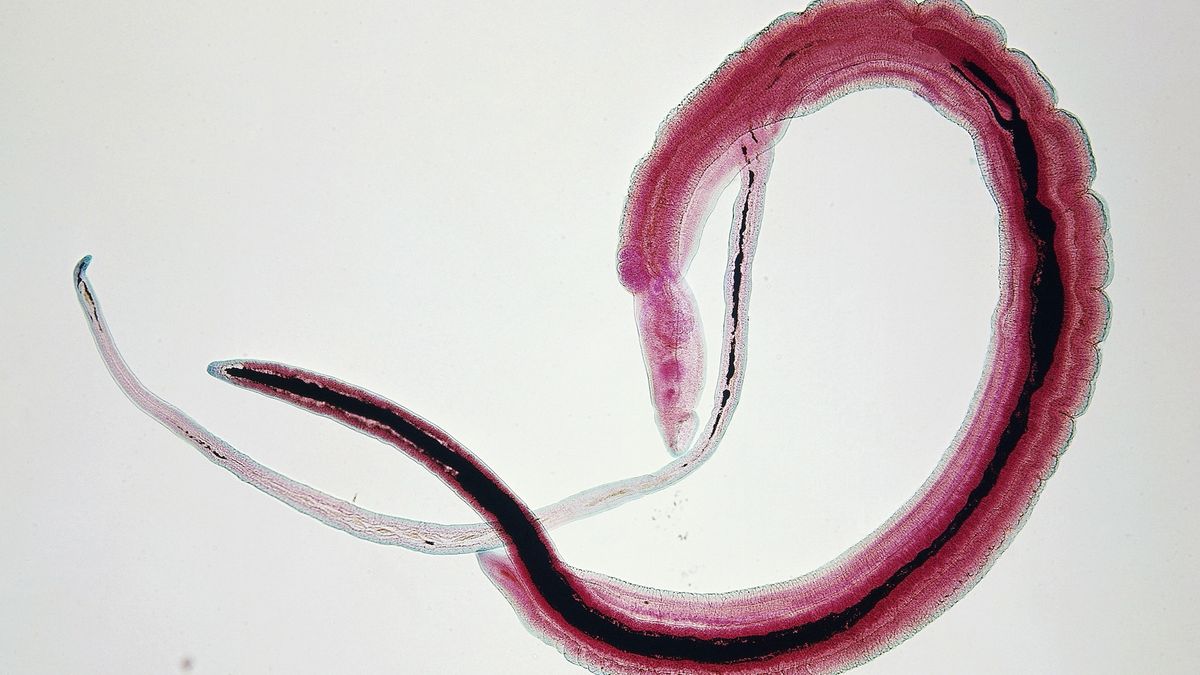
In a groundbreaking discovery, researchers have uncovered how a parasitic worm might potentially contribute to an increased risk of cervical cancer, while acknowledging that Human Papillomavirus (HPV) remains the primary cause of the disease.
Scientists have identified several intriguing mechanisms through which these parasitic organisms could potentially interact with cervical tissues, potentially creating an environment more susceptible to cancer development. This fascinating research sheds new light on the complex interactions between parasitic infections and cellular changes that might predispose individuals to cancer.
While HPV continues to be recognized as the principal driver of cervical cancer, this emerging research suggests that parasitic worms could play a more nuanced role in cancer risk than previously understood. The findings highlight the importance of comprehensive research in understanding the multifaceted nature of cancer development and potential risk factors.
Further investigation is needed to fully comprehend the relationship between parasitic worms and cervical cancer, but this research represents an exciting step forward in our understanding of potential cancer risk mechanisms.
Unraveling the Hidden Threat: Parasitic Worms and Cervical Cancer Risk
In the intricate landscape of medical research, scientists continue to uncover surprising connections between seemingly unrelated biological phenomena. The relationship between parasitic organisms and cancer development represents a fascinating frontier of medical investigation, challenging our understanding of disease progression and potential risk factors.Breakthrough Insights Reveal Shocking Cancer Connection You Can't Ignore!
The Complex Interplay of Parasitic Organisms and Cellular Transformation
Medical researchers have recently illuminated a profound and intricate relationship between parasitic worms and cervical cancer development. While human papillomavirus (HPV) remains the primary driver of this devastating disease, emerging evidence suggests that parasitic organisms may play a more complex role in cancer progression than previously understood. Parasitic infections create a unique microenvironment within human tissues that can potentially modify cellular mechanisms. These microscopic invaders can trigger inflammatory responses, alter immune system functioning, and potentially create conditions that make cells more susceptible to malignant transformation. The delicate balance between host immune response and parasitic survival creates a complex biological landscape that researchers are only beginning to comprehend.Molecular Mechanisms of Parasitic Influence on Cancer Development
The intricate molecular interactions between parasitic organisms and human cells reveal a sophisticated mechanism of potential cancer risk enhancement. Parasitic worms can potentially manipulate cellular signaling pathways, disrupt normal immune surveillance, and create conditions that might facilitate abnormal cell growth. Scientific investigations have demonstrated that certain parasitic infections can induce chronic inflammation, a known precursor to potential cancer development. This inflammatory response can lead to DNA damage, genetic mutations, and compromised cellular repair mechanisms. The prolonged presence of parasitic organisms might create a persistent state of cellular stress that could potentially increase cancer susceptibility.Immunological Implications and Future Research Directions
The intersection of parasitology and oncology presents a compelling area of scientific exploration. Researchers are increasingly recognizing that parasitic infections might not be simple passive events but active modulators of cellular environments. The immune system's response to these organisms could potentially create conditions that either suppress or inadvertently promote cancer development. Advanced molecular techniques and sophisticated imaging technologies are enabling scientists to map these complex interactions with unprecedented precision. By understanding the nuanced relationships between parasitic organisms and cellular transformation, researchers hope to develop more targeted prevention and intervention strategies.Clinical Implications and Patient Awareness
While the research remains preliminary, these findings underscore the importance of comprehensive health screenings and holistic approaches to understanding disease risk. Patients should maintain open dialogues with healthcare professionals, particularly in regions where parasitic infections are more prevalent. The potential link between parasitic worms and cervical cancer risk does not diminish the critical importance of HPV vaccination and regular medical screenings. Instead, it highlights the complex, multifaceted nature of cancer development and the ongoing need for sophisticated medical research.Global Health Perspectives and Research Challenges
These groundbreaking discoveries transcend individual medical disciplines, offering insights into the intricate relationships between parasitic organisms and human health. The research challenges traditional medical paradigms and emphasizes the need for interdisciplinary approaches to understanding disease mechanisms. International research collaborations are crucial in expanding our understanding of these complex biological interactions. By combining expertise from parasitology, oncology, immunology, and molecular biology, scientists can develop more comprehensive strategies for disease prevention and treatment.RELATED NEWS
Science

Lunar Frontier: China's Bold Plan for a Groundbreaking Telescope Beyond Earth's Horizon
2025-03-20 02:00:08
Science

Beyond AI: Flagship Pioneering's Bold Leap into Superintelligent Science
2025-03-10 15:29:00
Science

Code or No Code: California Pushes for Mandatory Computer Science in Schools
2025-04-10 13:00:00