Celestial Smiley: Venus and Jupiter Set to Create Cosmic Grin with Lunar Photobomb
Science
2025-04-18 13:00:00Content
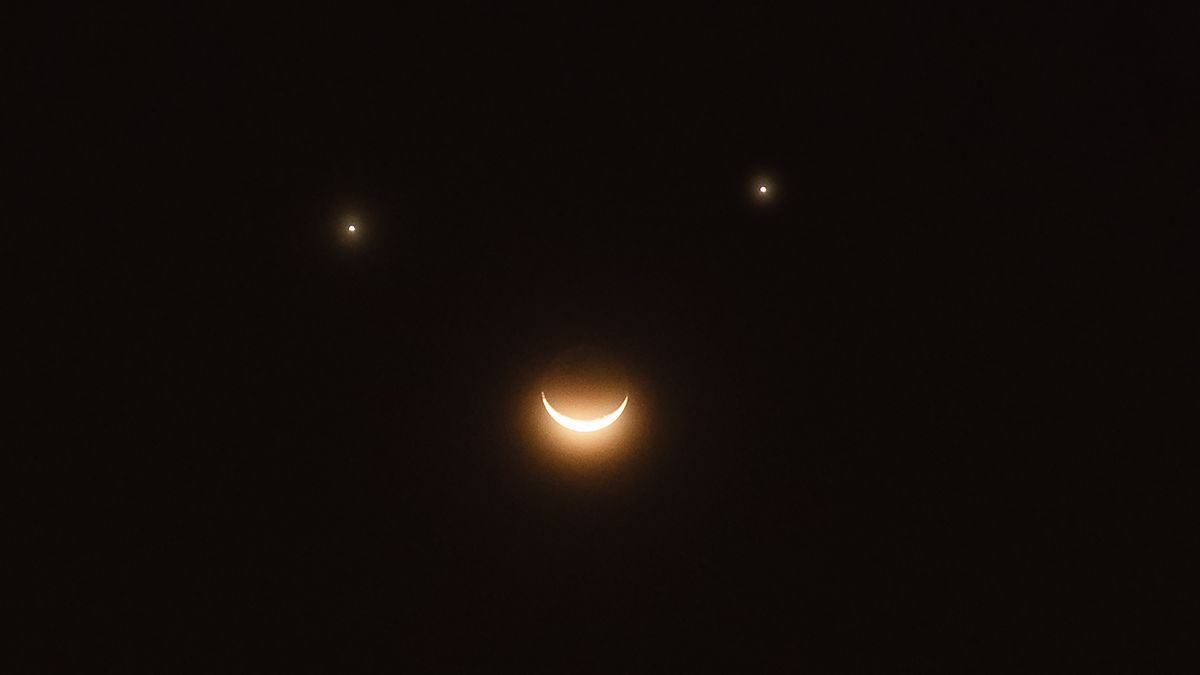

Stargazers and astronomy enthusiasts, get ready for a celestial spectacle! On April 25, the morning sky will come alive with a delightful cosmic phenomenon known as a rare "smiley face" triple conjunction. Venus, Saturn, and the delicate crescent moon will align in a mesmerizing formation, creating a stunning celestial smile just above the horizon.
This extraordinary astronomical event promises to be a visual treat for early risers and sky watchers. As the planets and moon nestle close together, they'll create a natural, whimsical pattern that looks remarkably like a grinning face peeking out from the dawn sky. Photographers and amateur astronomers will want to have their cameras and telescopes ready to capture this magical moment.
The conjunction offers a unique opportunity to witness the beauty and precision of our solar system's celestial dance. Whether you're a seasoned astronomer or simply someone who appreciates the wonders of the universe, this celestial smile is sure to brighten your morning and remind you of the incredible cosmic choreography happening right above our heads.
Celestial Symphony: A Rare Astronomical Dance Unveils Cosmic Artistry
In the vast, mysterious canvas of our universe, celestial events often unfold with breathtaking precision and unexpected beauty, offering humanity fleeting glimpses into the intricate choreography of cosmic bodies that transcend our earthly understanding.Witness the Extraordinary: When Planets and Moon Converge in Celestial Harmony
The Astronomical Phenomenon of Planetary Alignment
The morning sky on April 25th promises an extraordinary spectacle that will captivate astronomers, stargazers, and casual observers alike. This rare celestial event represents more than just a visual marvel; it's a testament to the complex gravitational interactions and orbital dynamics that govern our solar system. Venus and Saturn, two of the most luminous planetary bodies, will converge with the delicate crescent moon, creating a mesmerizing geometric configuration that occurs with remarkable infrequency. Astronomical alignments like these are not merely random occurrences but intricate mathematical dance sequences choreographed by gravitational forces spanning millions of kilometers. The precise positioning of these celestial bodies requires complex calculations involving orbital mechanics, planetary trajectories, and astronomical observation techniques that have been refined over centuries of scientific exploration.Understanding Planetary Conjunctions: A Scientific Perspective
Planetary conjunctions represent moments when celestial bodies appear to converge from Earth's perspective, creating visual alignments that fascinate both professional astronomers and amateur sky watchers. These events are more than aesthetic experiences; they provide critical opportunities for scientific observation and understanding of planetary movements. The upcoming conjunction involving Venus, Saturn, and the moon offers a unique window into the dynamic nature of our solar system. Venus, known for its brilliant luminosity, will shine with exceptional radiance, while Saturn's distinctive rings will add complexity to the visual landscape. The crescent moon, acting as a natural frame, will enhance the overall astronomical composition, creating what experts describe as a "cosmic smile" across the morning horizon.Observational Techniques and Viewing Recommendations
To fully appreciate this rare astronomical event, observers will need specific equipment and strategic positioning. High-quality telescopes with wide-angle lenses can capture the intricate details of the planetary alignment, while binoculars offer a more accessible viewing option for casual enthusiasts. The optimal viewing window occurs during the early morning hours, specifically around astronomical twilight when the sky begins to brighten but remains dark enough to highlight celestial bodies. Professional astronomers recommend selecting locations with minimal light pollution, preferably elevated areas with unobstructed eastern horizons. Urban observers might face challenges due to atmospheric interference and artificial lighting, making rural or suburban locations significantly more conducive to experiencing this celestial spectacle.Historical and Cultural Significance of Celestial Alignments
Throughout human history, astronomical events have held profound cultural and spiritual significance. Ancient civilizations interpreted planetary conjunctions as divine messages, celestial omens, or markers of significant temporal transitions. From Mayan astronomers to Babylonian sky watchers, humans have consistently found deep meaning in the movements of celestial bodies. This particular alignment carries scientific significance beyond its visual appeal. It represents a moment of cosmic synchronicity, where planetary orbits momentarily converge from our terrestrial perspective, offering a glimpse into the intricate mathematical precision governing our solar system's architecture.Technological Advancements in Astronomical Observation
Modern technology has revolutionized our ability to observe and understand such astronomical phenomena. Advanced telescopes, satellite imaging, and computational modeling allow scientists to predict and analyze planetary movements with unprecedented accuracy. The upcoming Venus-Saturn-moon conjunction will be documented using cutting-edge technologies, providing researchers with valuable data about planetary dynamics and orbital mechanics. Emerging technologies like adaptive optics and space-based observatories continue to expand our understanding of these celestial events, transforming what were once mysterious occurrences into comprehensible scientific phenomena that reveal the underlying mathematical elegance of our universe.RELATED NEWS
Science

Breaking: Sci-Fi Becomes Reality - Researchers Unveil Touchable 3D Holographic Breakthrough
2025-04-23 02:49:32
Science

Science Unfiltered: Decoding Life's First Spark, Avian Linguistics, and TikTok's ADHD Blind Spot
2025-03-20 22:16:34
Science

Young Innovators Unleash Cutting-Edge Science: Fresno County's Future Researchers Take Center Stage
2025-03-20 14:56:20