Green Revolution: 50% of Americans Ready to Ditch Meat for Planet's Sake
Environment
2025-04-17 17:57:21Content

In a recent survey revealing growing environmental consciousness, nearly half of the participants expressed a willingness to embrace plant-based eating as a meaningful strategy to combat climate change. Specifically, 46% of respondents indicated they would seriously consider adopting a plant-based diet to help reduce greenhouse gas emissions, signaling a significant shift in consumer attitudes towards sustainable food choices.
This compelling statistic highlights the increasing awareness of how individual dietary decisions can have a tangible impact on global environmental challenges. By choosing plant-based meals, consumers recognize they can play a direct role in lowering carbon footprints and supporting more sustainable food systems.
The survey results suggest a promising trend: more people are becoming aware of the environmental benefits of reducing meat consumption and exploring plant-based alternatives. As climate concerns continue to grow, dietary choices are emerging as a powerful tool for personal environmental action.
Green Revolution: How Plant-Based Diets Are Transforming Climate Action
In an era of escalating environmental challenges, consumers are increasingly recognizing their potential to combat climate change through conscious dietary choices. The intersection of personal nutrition and global sustainability has emerged as a powerful catalyst for meaningful environmental transformation, challenging traditional perspectives on individual impact.Revolutionize Your Plate, Rescue the Planet
The Climate Crisis and Dietary Transformation
The global food system represents a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, accounting for approximately 26-33% of total worldwide environmental impact. Researchers have extensively documented the substantial carbon footprint associated with traditional animal agriculture, revealing that meat and dairy production generate substantially higher emissions compared to plant-based alternatives. Sophisticated agricultural modeling demonstrates that transitioning toward plant-centric diets could potentially reduce individual carbon footprints by up to 73%, representing a transformative strategy for mitigating climate change. Emerging scientific consensus suggests that dietary choices represent more than personal nutrition—they constitute a critical environmental intervention. Complex agricultural ecosystems interact dynamically, with livestock production generating methane, nitrous oxide, and carbon dioxide at unprecedented rates. By reimagining nutritional frameworks, individuals can directly participate in global sustainability efforts, transforming personal consumption into a meaningful climate action strategy.Psychological Drivers of Dietary Sustainability
Consumer motivations for embracing plant-based nutrition extend beyond environmental considerations, encompassing intricate psychological and social dynamics. Behavioral research indicates that environmental consciousness increasingly influences dietary decisions, with younger generations demonstrating heightened sensitivity to sustainability implications. Millennials and Generation Z consistently report stronger correlations between personal values and consumption patterns, suggesting a fundamental shift in societal perspectives toward holistic environmental responsibility. Psychological studies reveal that individuals perceiving themselves as change agents are more likely to adopt transformative dietary practices. This self-perception transforms dietary choices from mere nutritional decisions into powerful statements of environmental commitment. The emerging narrative positions plant-based consumption as an accessible, impactful mechanism for individual climate engagement.Nutritional Innovation and Culinary Evolution
Contemporary plant-based alternatives have transcended traditional limitations, offering sophisticated, nutritionally comprehensive options that challenge conventional dietary paradigms. Technological advancements in food science have generated plant-based proteins mimicking traditional meat textures and flavors with remarkable precision, making sustainable nutrition increasingly appealing to mainstream consumers. Culinary innovation represents a critical component of this dietary revolution. Renowned chefs and food technologists collaborate to develop plant-based cuisines that are not merely environmentally responsible but genuinely delectable. This gastronomic transformation dismantles historical perceptions of plant-based diets as restrictive or bland, presenting sustainability as an exciting, flavorful lifestyle choice.Economic and Environmental Implications
The widespread adoption of plant-based diets carries profound economic and environmental ramifications. Agricultural economists project significant potential for reduced resource consumption, with plant-based protein production requiring substantially less water, land, and energy compared to traditional animal agriculture. These efficiency gains translate into considerable environmental benefits, potentially mitigating substantial portions of global greenhouse gas emissions. Market analyses indicate exponential growth in plant-based food sectors, reflecting increasing consumer awareness and technological sophistication. Investment trends suggest that sustainable nutrition represents not just an environmental imperative but a significant economic opportunity, driving innovation across agricultural and technological domains.Global Policy and Systemic Transformation
International policy frameworks are progressively recognizing dietary choices as critical climate mitigation strategies. Governmental and non-governmental organizations increasingly promote plant-based nutrition as a complementary approach to technological and industrial emissions reduction efforts. This holistic perspective acknowledges individual consumption patterns as integral to comprehensive climate action strategies. Collaborative initiatives between scientific institutions, governmental bodies, and private sector entities are developing educational programs and policy frameworks that support sustainable dietary transitions. These multifaceted approaches aim to provide consumers with comprehensive information, resources, and incentives for making environmentally conscious nutritional choices.RELATED NEWS
Environment
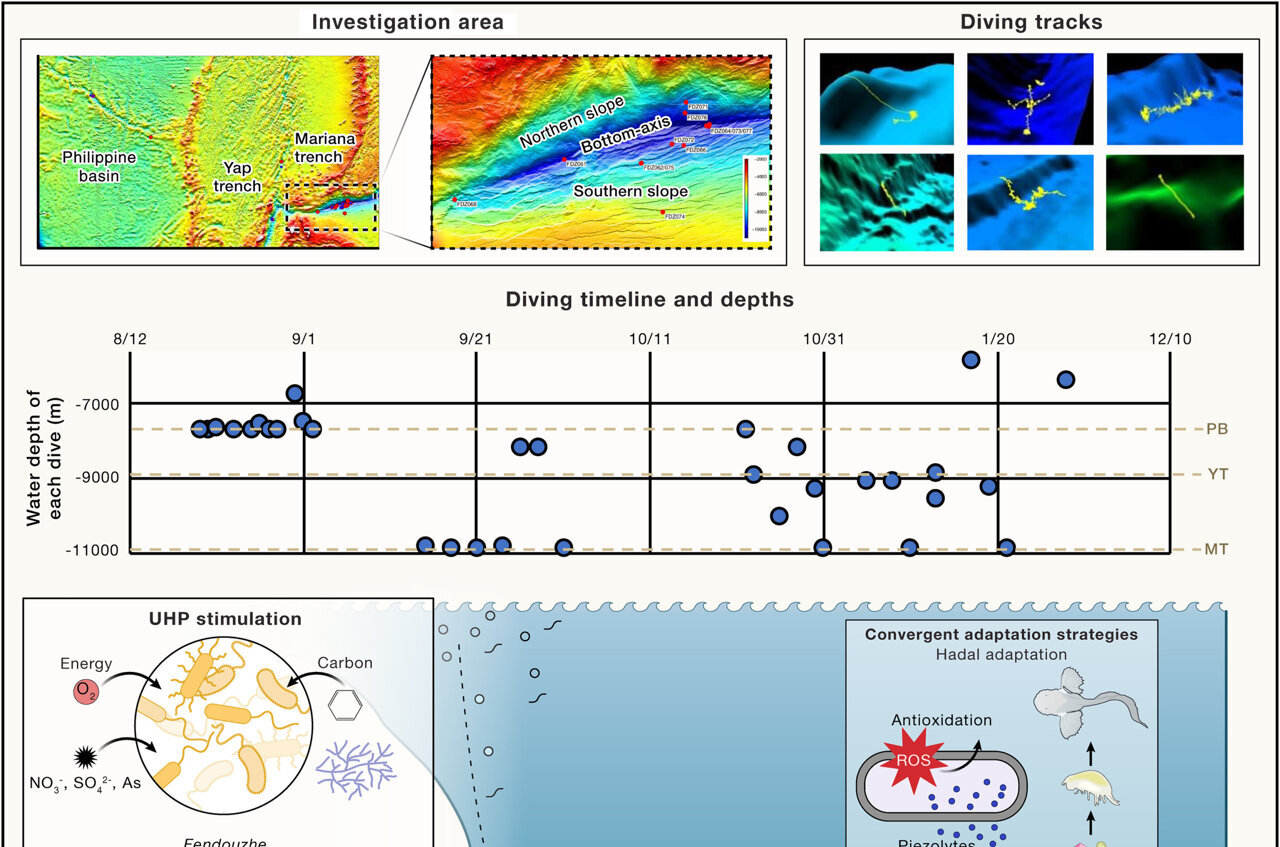
Alien-Like Creatures Emerge: Scientists Unveil Mysterious Life Thriving in Earth's Deepest Abyss
2025-03-10 15:40:01
Environment

Wildlife Advocates Urge Lincolnshire's New Mayor: Nature Must Lead the Way
2025-04-29 05:17:24
Environment

Environmental Communities Left Behind: Trump's Controversial Grant Cuts Spark Outrage
2025-04-14 09:00:30





