Alien Life Breakthrough: Astronomers Detect Potential Biosignature in Distant Star System
Science
2025-04-17 14:32:01Content
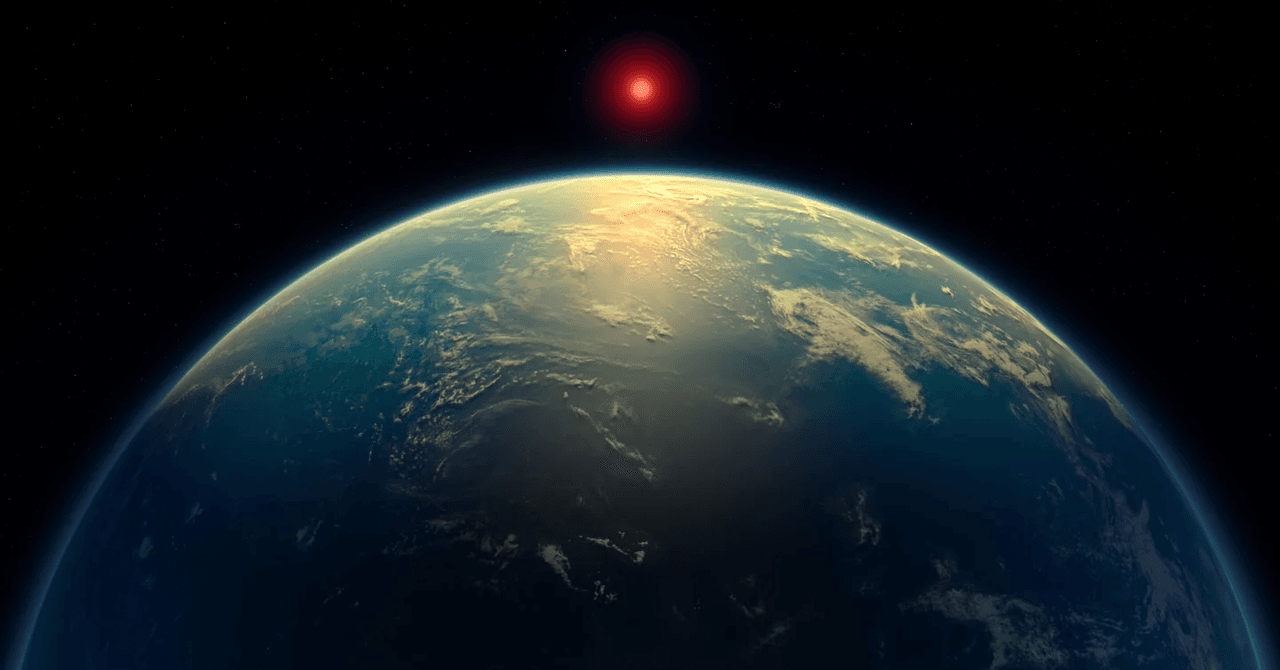
In a groundbreaking discovery, astronomers using the cutting-edge James Webb Space Telescope have uncovered tantalizing evidence of potential life on the distant exoplanet K2-18b. The scientific team detected traces of dimethyl sulfide, a fascinating chemical compound that could signal the presence of marine microorganisms.
This remarkable finding marks a significant milestone in the search for extraterrestrial life. Dimethyl sulfide is typically associated with biological processes on Earth, particularly those occurring in marine environments. Its presence on K2-18b suggests the possibility of primitive life forms existing in the planet's potentially habitable conditions.
The James Webb Space Telescope, renowned for its unprecedented observational capabilities, has once again pushed the boundaries of our understanding of distant worlds. By capturing detailed spectroscopic data, scientists have opened up new possibilities in the exploration of potentially life-supporting planets beyond our solar system.
While this discovery is not definitive proof of life, it represents an exciting step forward in humanity's quest to understand whether we are alone in the universe. Researchers are eager to conduct further investigations to confirm and expand upon these intriguing initial findings.
Cosmic Whispers: Unveiling Potential Life Signatures on a Distant Exoplanet
In the vast, enigmatic expanse of the universe, humanity's quest to understand our cosmic neighborhood has taken a remarkable leap forward. The James Webb Space Telescope, a marvel of human engineering and scientific curiosity, has pierced the veil of interstellar mystery, revealing tantalizing hints of potential biological activity on a distant world that challenges our understanding of life's possibilities.Breakthrough Discovery: When Science Meets Extraordinary Possibility
The Extraordinary Planet K2-18b: A Cosmic Enigma
The exoplanet K2-18b represents a fascinating astronomical anomaly that has captured the imagination of scientists worldwide. Located in a distant solar system, this celestial body defies conventional planetary classifications, existing in a unique zone that challenges our traditional understanding of planetary environments. Researchers have long been intrigued by its complex atmospheric composition and potential habitability, making it a prime target for advanced astronomical investigations. The planet's unique characteristics stem from its position within the habitable zone of its host star, a region where temperatures could potentially support liquid water—a fundamental prerequisite for life as we understand it. Unlike many exoplanets that are either scorching hot or freezing cold, K2-18b occupies a delicate balance that makes it an extraordinary candidate for potential biological activity.Dimethyl Sulfide: A Potential Biosignature of Cosmic Proportions
The detection of dimethyl sulfide represents a groundbreaking moment in astronomical research. This specific molecular compound is typically associated with marine microorganism activities on Earth, making its presence on K2-18b an extraordinary scientific revelation. The James Webb Space Telescope's advanced spectroscopic instruments have provided unprecedented insights into the planet's atmospheric chemistry, allowing scientists to identify this potential biosignature with remarkable precision. Dimethyl sulfide's significance cannot be overstated. On our planet, this molecule is predominantly produced by marine phytoplankton, serving as a critical indicator of biological processes. Its detection on K2-18b suggests the tantalizing possibility of similar biological mechanisms occurring on this distant world, opening up profound questions about the nature and potential diversity of life in the universe.Technological Marvel: The James Webb Space Telescope's Role
The James Webb Space Telescope represents the pinnacle of human technological achievement in astronomical observation. Equipped with cutting-edge infrared capabilities and unprecedented sensitivity, this remarkable instrument has revolutionized our ability to study distant celestial bodies with extraordinary detail and precision. Unlike previous telescopes, the Webb telescope can analyze the chemical composition of exoplanet atmospheres by examining the subtle variations in light as it passes through these distant planetary envelopes. This technique, known as spectroscopic analysis, allows scientists to detect molecular signatures that might indicate the presence of biological processes, transforming our understanding of potential extraterrestrial environments.Implications for Astrobiology and Future Exploration
The discovery on K2-18b transcends mere scientific curiosity, representing a potential paradigm shift in our understanding of life's potential diversity. While the presence of dimethyl sulfide does not conclusively prove biological activity, it provides the most compelling evidence to date of potential life-supporting conditions beyond Earth. This breakthrough encourages scientists to reconsider existing models of planetary habitability and biological emergence. It suggests that life might develop through mechanisms and in environments dramatically different from those we currently comprehend, expanding the conceptual boundaries of what we consider possible in the vast cosmic landscape. The research surrounding K2-18b opens numerous avenues for future exploration, inspiring a new generation of astronomers and astrobiologists to push the boundaries of human knowledge. Each discovery brings us closer to answering fundamental questions about our place in the universe and the potential diversity of life beyond our home planet.RELATED NEWS
Science

Science Under Siege: How Trump's Policy Rollbacks Could Derail Climate Action and Endanger Public Health
2025-05-05 11:24:44
Science
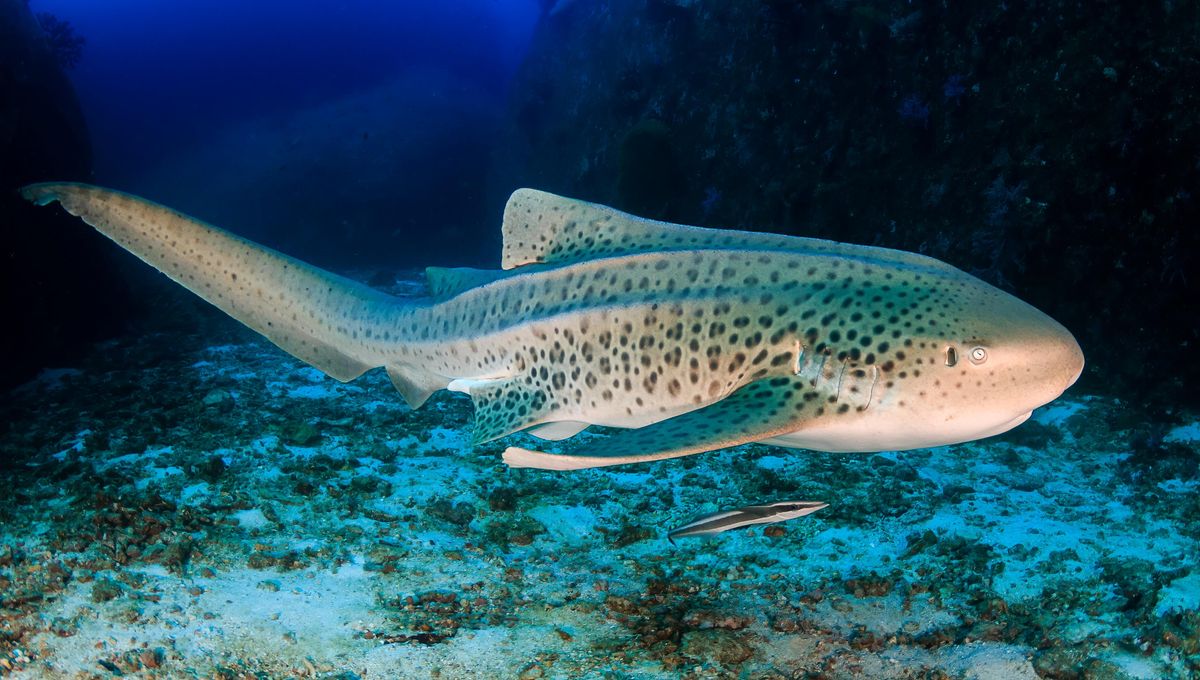

Breakthrough Marine Science: Researchers Develop Innovative Technique to Assist Shark Reproduction
2025-03-01 11:18:34