Monkey Business Banned: Gregg County Drops the Hammer on Primate Presence
Health
2025-04-16 00:36:44Content

In a groundbreaking move to protect wildlife and ensure public safety, local authorities have implemented a comprehensive ordinance that strictly prohibits the ownership of primates within city limits. The regulation extends beyond just chimpanzees, encompassing a wide range of primate species to prevent potential risks and challenges associated with exotic pet ownership.
The ordinance reflects growing concerns about the complex needs of primates and the potential dangers they pose when kept in domestic environments. Experts have long argued that these intelligent and highly social animals require specialized care that most households cannot provide. From capuchin monkeys to baboons, the ban covers a comprehensive list of primate species, ensuring a uniform approach to wildlife protection.
Residents who currently own primates will be given a reasonable transition period to rehome their animals through authorized wildlife sanctuaries or specialized facilities. The goal is not to punish pet owners but to prioritize the well-being of both the animals and the community.
Local wildlife officials emphasize that this ordinance is part of a broader commitment to responsible animal management and public safety. By preventing the private ownership of primates, the city aims to reduce potential health risks, prevent animal welfare issues, and protect both human and animal populations.
Primate Prohibition: Local Ordinance Sparks Controversy in Urban Wildlife Management
In an unprecedented move that has caught the attention of animal rights activists and urban planners alike, a groundbreaking local ordinance has emerged, challenging the conventional boundaries of wildlife interaction within municipal limits. This regulatory decision represents a complex intersection of public safety, environmental considerations, and community governance.When Urban Regulations Redefine Human-Animal Boundaries
The Comprehensive Primate Restriction Landscape
The recently implemented ordinance represents a nuanced approach to urban wildlife management, extending far beyond simple regulatory constraints. Municipal authorities have meticulously crafted a comprehensive framework that addresses the intricate challenges of primate presence within city limits. Experts suggest that such regulations stem from multifaceted concerns including public health risks, potential ecological disruptions, and the complex dynamics of human-animal coexistence. Researchers and wildlife management professionals have long debated the implications of primate interactions in urban environments. The ordinance reflects a proactive stance, acknowledging the potential risks associated with unregulated primate populations. These risks encompass disease transmission, property damage, and unpredictable behavioral patterns that could compromise community safety.Ecological and Public Safety Considerations
The prohibition extends comprehensively across various primate species, demonstrating a holistic approach to urban wildlife management. Municipal legislators have conducted extensive consultations with primatologists, environmental scientists, and public health experts to develop a nuanced regulatory framework. This collaborative approach ensures that the ordinance is not merely a restrictive measure but a scientifically informed strategy for maintaining ecological balance. Urban ecosystems are delicate, interconnected environments where human activities and wildlife interactions require careful navigation. The primate restriction represents a critical intervention designed to mitigate potential conflicts and protect both human residents and animal populations. By establishing clear boundaries, the municipality aims to create a sustainable model of coexistence that prioritizes safety and ecological integrity.Legal and Ethical Implications of Wildlife Regulation
The ordinance raises profound questions about the legal and ethical dimensions of wildlife management in urban settings. Legal experts argue that such regulations represent a sophisticated approach to balancing individual freedoms with collective community interests. The comprehensive nature of the restriction suggests a forward-thinking perspective that anticipates potential challenges rather than merely reacting to existing problems. Ethical considerations play a crucial role in understanding the broader context of this regulatory decision. The ordinance reflects a growing recognition of the complex relationships between human societies and wildlife populations. By establishing clear guidelines, municipal authorities aim to create a framework that respects both ecological diversity and community safety.Community Response and Future Perspectives
Initial community responses to the ordinance have been diverse and nuanced. Some residents applaud the proactive approach to wildlife management, while others express concerns about potential overreach. This dynamic dialogue underscores the complexity of urban environmental governance and the ongoing negotiation between human interests and ecological considerations. Wildlife management experts suggest that this ordinance could serve as a potential model for other municipalities grappling with similar challenges. The comprehensive and scientifically informed approach demonstrates a sophisticated understanding of the intricate relationships between urban environments and wildlife populations. The implementation of such regulations represents a critical moment in urban environmental policy, signaling a shift towards more holistic and proactive approaches to wildlife management. As cities continue to expand and ecological boundaries become increasingly complex, such ordinances will likely become more prevalent, reflecting a growing understanding of the delicate balance between human development and natural ecosystems.RELATED NEWS
Health
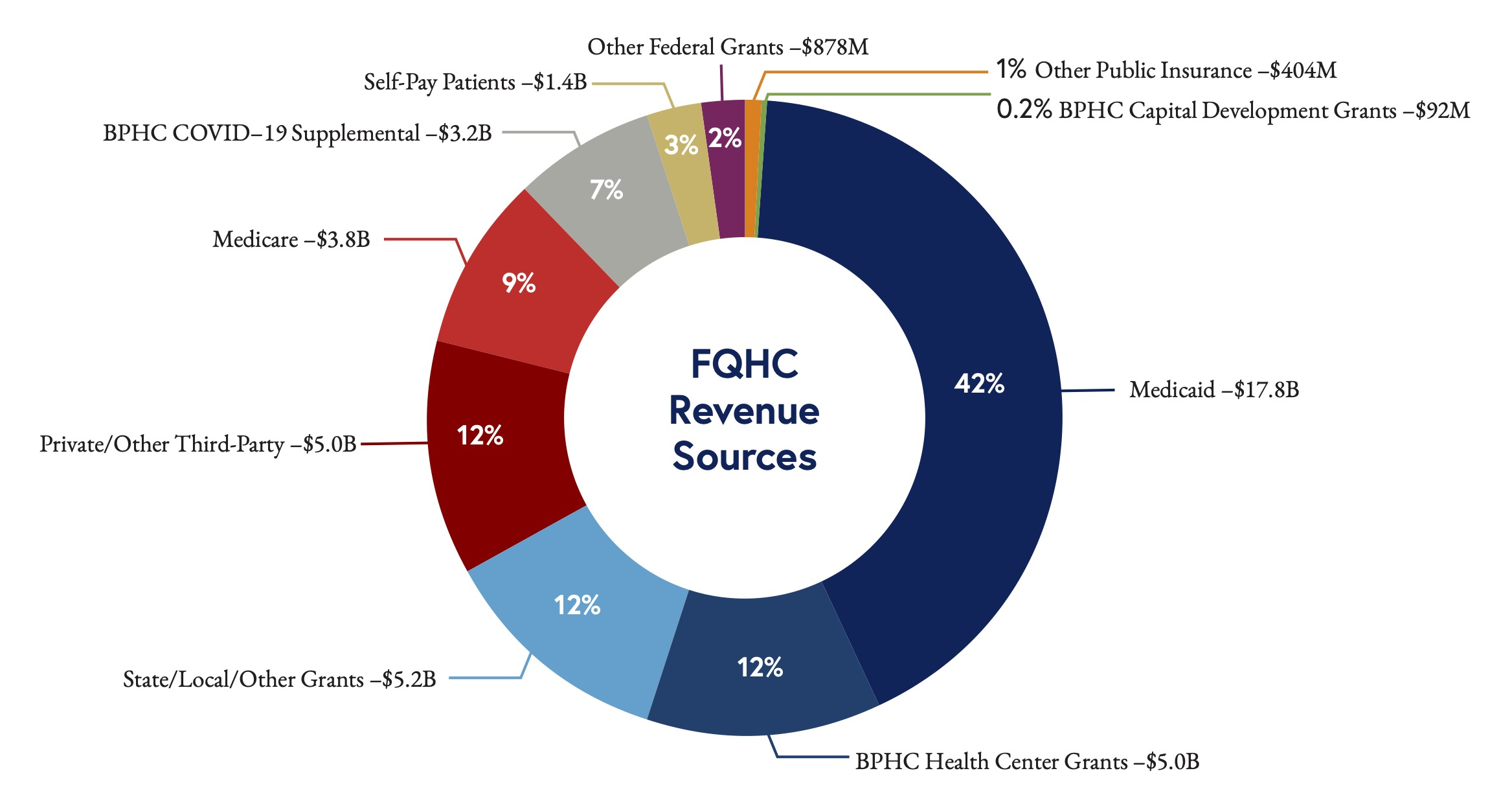
Breaking: Community Health Centers Revolutionize Patient Care Through Value-Based Strategies
2025-02-25 18:06:34
Health

Turning the Tide: Independence Health Narrows Financial Gaps Despite Persistent Headwinds
2025-02-25 18:47:44