Deep-Sea Resurrection: Ancient Microbe Awakens After Millennia in Oceanic Darkness
Science
2025-04-13 20:30:24Content
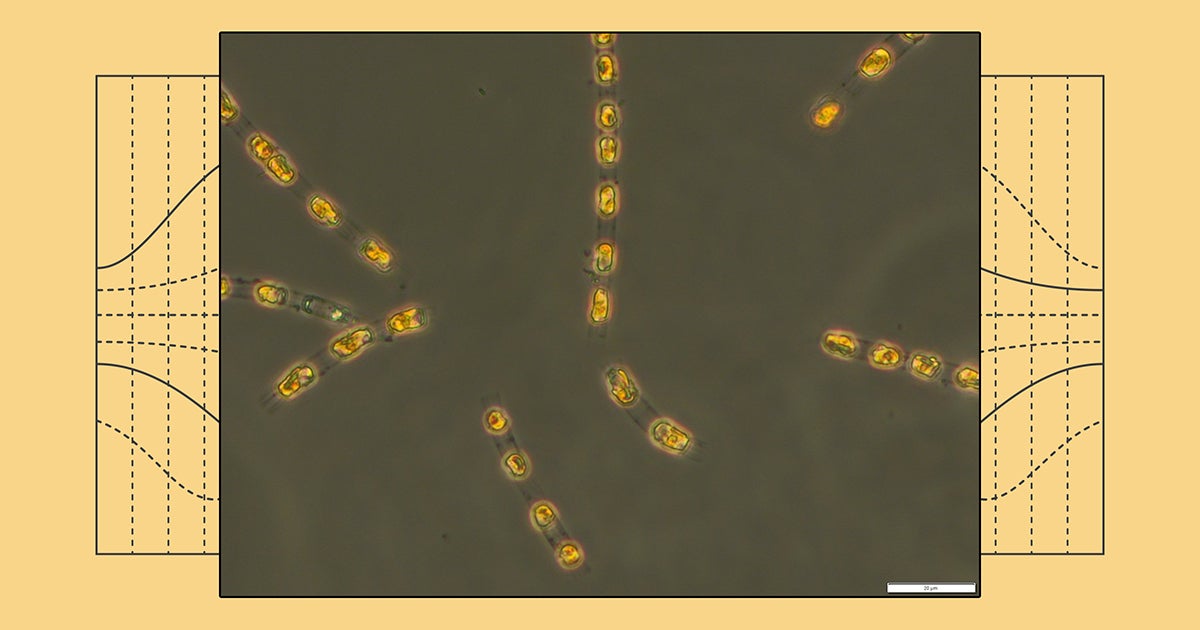
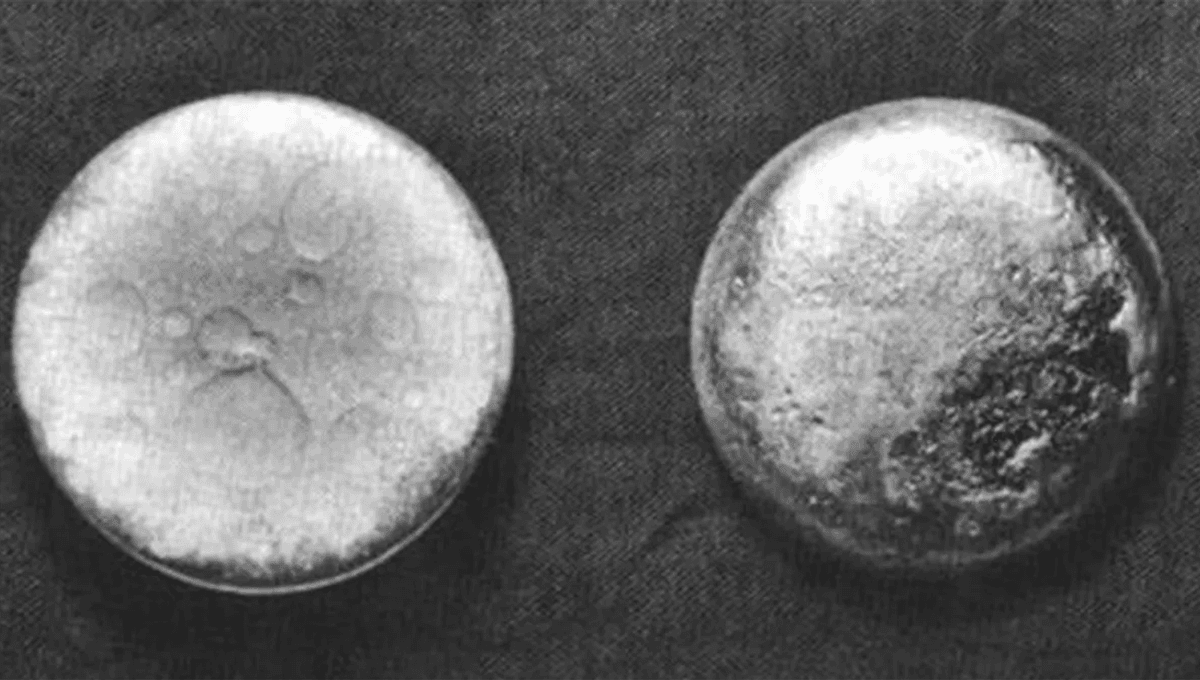
Ancient Algae Awakens: A 7,000-Year Journey from Dormancy to Life
In a remarkable scientific breakthrough, researchers in Germany have accomplished the seemingly impossible: reviving microscopic algae cells that have been entombed at the bottom of the Baltic Sea for over 7,000 years. These resilient organisms, trapped beneath layers of sediment and deprived of oxygen and light for millennia, have defied all expectations by springing back to life with astonishing vigor.
Published in The ISME Journal, the study reveals that once these ancient cells were carefully extracted and reanimated, they demonstrated full biological functionality. Like time travelers awakening from a deep slumber, the algae immediately resumed their critical role in oxygen production and began multiplying with remarkable ease.
This extraordinary discovery represents the oldest known organism to be successfully revived, offering unprecedented insights into the incredible survival capabilities of microscopic life forms. The research not only challenges our understanding of biological resilience but also opens up fascinating possibilities for studying how organisms can endure extreme environmental conditions.
Resurrection of Ancient Algae: A Miraculous Discovery in Marine Biology
In the depths of scientific exploration, researchers have uncovered a remarkable phenomenon that challenges our understanding of biological preservation and cellular resilience. The Baltic Sea, a silent keeper of ancient secrets, has revealed a stunning scientific breakthrough that pushes the boundaries of what we previously believed possible about life's endurance.Defying Time: When Microscopic Life Refuses to Surrender
The Extraordinary Preservation of Cellular Life
Marine biologists have long been fascinated by the potential for life to survive in extreme conditions, but the recent discovery in the Baltic Sea represents an unprecedented milestone in scientific understanding. Deep beneath layers of sedimentary rock, microscopic algae cells have maintained their fundamental biological integrity for thousands of years, presenting a testament to the remarkable adaptability of living organisms. The sedimentary environment of the Baltic Sea created a unique preservation chamber, effectively suspending these algae cells in a state of suspended animation. Unlike typical biological specimens that deteriorate rapidly, these cells remained completely intact, protected from external environmental influences by dense layers of geological material.Cellular Resurrection: A Scientific Marvel
When researchers carefully extracted these ancient algae cells from their millennia-long slumber, they were astounded by the organisms' capacity for immediate revival. Upon reintroduction to suitable environmental conditions, the cells demonstrated an extraordinary ability to restart metabolic processes, rapidly generating oxygen and initiating cellular reproduction. This phenomenon challenges fundamental assumptions about cellular longevity and biological dormancy. The algae's ability to remain viable after more than 7,000 years suggests potential implications for understanding preservation mechanisms in various biological systems, from medical research to potential extraterrestrial life studies.Implications for Scientific Understanding
The discovery opens numerous research pathways across multiple scientific disciplines. Microbiologists, marine researchers, and cellular biologists are now examining the molecular mechanisms that allowed these algae cells to maintain their structural and functional integrity over such an extended period. Potential applications of this research could revolutionize our understanding of cellular preservation techniques, potentially offering insights into medical treatments, agricultural innovations, and even strategies for long-term biological storage. The resilience demonstrated by these ancient algae cells suggests that life possesses far more adaptive capabilities than previously understood.Technological and Research Methodologies
Advanced extraction and revival techniques were crucial in this groundbreaking research. Specialized laboratory protocols ensured minimal cellular damage during the retrieval and reanimation processes. Cutting-edge microscopic imaging and genetic analysis provided researchers with unprecedented insights into the cellular structures that enabled such remarkable preservation. The interdisciplinary nature of this research highlights the importance of collaborative scientific approaches. By combining expertise from marine biology, microbiology, and geological sciences, researchers were able to unlock a mystery that had remained hidden for thousands of years.Environmental and Ecological Perspectives
Beyond the immediate scientific implications, this discovery offers profound insights into environmental adaptation and resilience. The algae's survival mechanism provides a unique window into understanding how microscopic organisms can endure extreme conditions, potentially offering clues about climate change adaptation and ecosystem survival strategies. The research team's meticulous documentation and analysis, published in The ISME Journal, represents a significant contribution to our collective scientific knowledge, demonstrating once again that the natural world continues to surprise and inspire us with its incredible complexity and endurance.RELATED NEWS

Mushroom Mystery: How a Citizen Science App Became a Key Player in a Deadly Dinner Party Investigation







