Beyond Earth's Horizon: How Space Science is Launching a Trillion-Dollar Economic Frontier
Science
2025-04-11 20:57:24Content
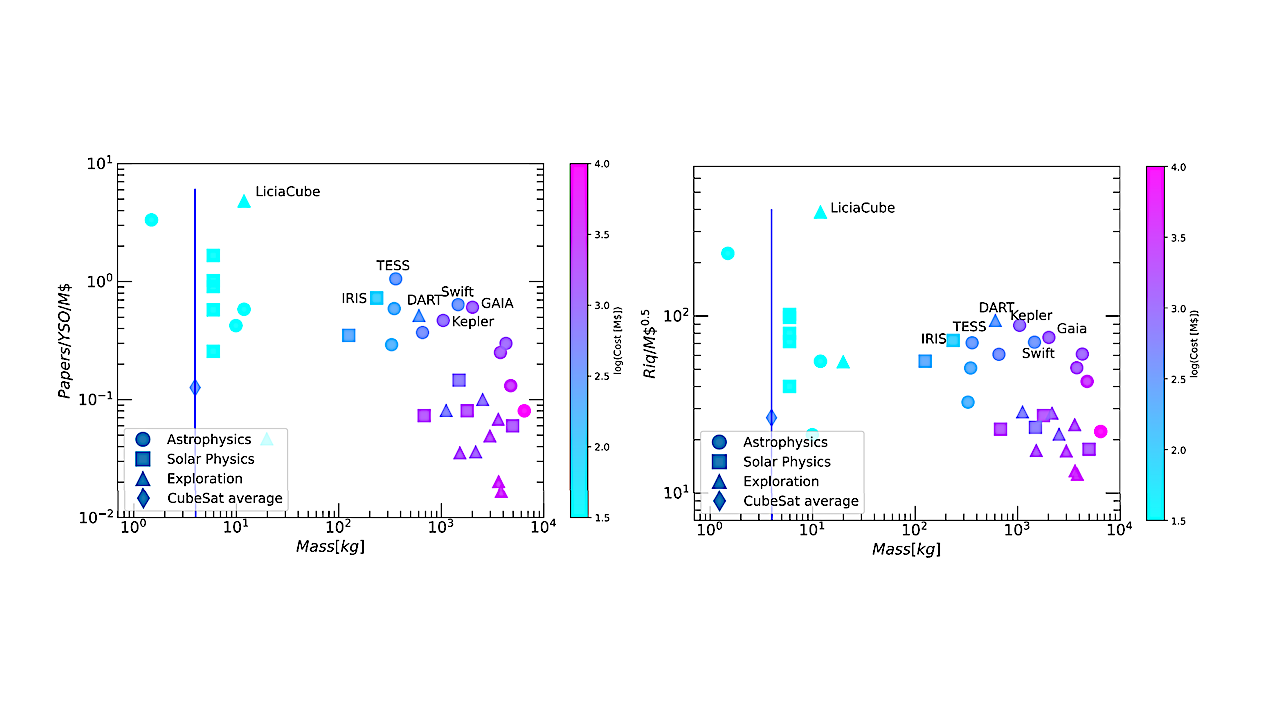
The Future of Astronomical Exploration: Balancing Ambition and Cost
As we stand on the cusp of unprecedented technological advancement, a critical question looms large in the scientific community: Can we continue to pursue groundbreaking space missions dedicated to fundamental scientific research? Iconic observatories like the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), Chandra X-ray Observatory, and James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) have revolutionized our understanding of the universe, but their astronomical price tags raise serious concerns about future large-scale scientific endeavors.
These remarkable instruments have pushed the boundaries of human knowledge, revealing cosmic mysteries that were once unimaginable. However, the escalating costs of such missions are forcing scientists and policymakers to confront a challenging dilemma. The complexity of cutting-edge space technology, combined with increasingly sophisticated scientific requirements, drives development expenses to unprecedented heights.
While technological innovation continues to advance, funding constraints and economic challenges threaten to limit our ability to launch similarly ambitious projects. The scientific community must now explore creative solutions – from international collaborations and more efficient design strategies to leveraging emerging technologies that could dramatically reduce mission costs.
The stakes are high. Each of these observatories has provided transformative insights into our universe, from revealing distant galaxies to understanding complex astronomical phenomena. The potential loss of such exploratory capabilities would represent a significant setback for human scientific progress.
As we look to the future, the challenge lies in finding a delicate balance between scientific ambition and economic feasibility. Will innovation and collaborative approaches pave the way for continued deep-space exploration, or will financial constraints ground our most audacious scientific dreams?
The Future of Space Exploration: Navigating the Economic and Scientific Frontiers
In the vast expanse of human curiosity, space exploration stands as a testament to our relentless pursuit of knowledge and technological advancement. As we stand on the precipice of a new era in cosmic research, the challenges and opportunities facing large-scale scientific space missions have never been more complex or compelling.Pushing the Boundaries of Human Understanding Beyond Earth's Horizons
The Economic Landscape of Space Science
The astronomical costs associated with space missions have long been a critical point of contention among scientific communities, policymakers, and funding agencies. Telescopes like Hubble, Chandra, and James Webb have revolutionized our understanding of the universe, but their price tags run into billions of dollars. Modern space agencies must now navigate a delicate balance between scientific ambition and financial constraints. The economics of space exploration have dramatically transformed in recent years. Private companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin have introduced unprecedented cost-efficiency models, challenging traditional government-funded approaches. These innovations have opened new pathways for complex scientific missions, potentially democratizing access to space research in ways previously unimaginable.Technological Innovations Reshaping Space Mission Capabilities
Emerging technologies are fundamentally reimagining what's possible in space exploration. Advanced materials, miniaturization of scientific instruments, and breakthrough propulsion technologies are creating opportunities for more cost-effective and sophisticated missions. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are now integral to mission planning, data analysis, and predictive modeling, dramatically reducing human error and operational expenses. Quantum computing and advanced sensor technologies are providing unprecedented capabilities for scientific instruments. These technological leaps mean that future space missions could potentially achieve more complex scientific objectives with smaller, more efficient spacecraft, challenging the traditional paradigm of massive, expensive observatories.Global Collaboration and Funding Strategies
International scientific collaboration has emerged as a critical strategy for managing the astronomical costs of space missions. Multinational partnerships allow for risk-sharing, resource pooling, and collective scientific expertise. The success of projects like the International Space Station demonstrates the potential of cooperative approaches in overcoming financial and technological barriers. Innovative funding models are also gaining traction. Crowdfunding, public-private partnerships, and alternative investment strategies are providing new avenues for supporting ambitious space science projects. These approaches not only distribute financial risk but also increase public engagement and scientific literacy.The Human Factor in Space Exploration
Beyond technological and economic considerations, human curiosity remains the primary driver of space exploration. The fundamental human desire to understand our cosmic environment transcends financial calculations. Each mission represents a collective human endeavor to expand our knowledge and push the boundaries of scientific understanding. Psychological and sociological research suggests that space exploration serves deeper human needs beyond pure scientific inquiry. It represents hope, inspiration, and a tangible manifestation of human potential. This intrinsic value cannot be easily quantified but plays a crucial role in sustaining long-term scientific investments.Sustainable and Adaptive Mission Design
Future space missions must prioritize sustainability and adaptability. This means developing spacecraft and scientific instruments that can be upgraded, repaired, or repurposed. Modular design principles and advanced robotics could significantly extend mission lifespans and scientific capabilities while managing overall costs. The concept of adaptive missions represents a paradigm shift from traditional, single-purpose spacecraft to more flexible, multi-objective platforms. By designing missions that can evolve and respond to unexpected scientific discoveries, researchers can maximize the return on substantial investments. As we contemplate the future of space exploration, the path forward is neither straightforward nor predictable. It will require unprecedented collaboration, technological innovation, and a commitment to pushing the boundaries of human knowledge.RELATED NEWS
Science

Breaking: Visionary Mechanical Engineer Tapped to Helm Cutting-Edge Engineering College
2025-03-28 23:35:50
Science

Unsung Digital Archives: How Tiny Earth Science Databases Are Saving Our Planet's Secrets
2025-03-19 13:23:34