Extinct and Eager: The Wild Science of Bringing Prehistoric Predators Back to Life
Science
2025-04-08 16:25:00Content

In a bold scientific claim that has sparked intense debate, Colossal Biosciences has announced the "de-extinction" of the legendary dire wolf, a prehistoric predator that once roamed North America. However, the announcement has been met with significant skepticism from the scientific community.
While the company touts this as a groundbreaking achievement, many researchers argue that the hype surrounding de-extinction is diverting crucial resources and attention from more pressing conservation efforts. The dire wolf, made famous by popular culture like the HBO series "Game of Thrones," went extinct around 13,000 years ago and has long captured the imagination of both scientists and the public.
Experts in conservation biology are particularly concerned that the sensational narrative of bringing back extinct species is overshadowing the critical work of protecting currently endangered animals and their habitats. They warn that the immense financial and scientific investments required for de-extinction projects could be more effectively used to prevent existing species from disappearing forever.
The controversy highlights the complex ethical and scientific challenges of attempting to resurrect species that have long since vanished from the Earth, raising profound questions about the boundaries of scientific innovation and environmental preservation.
Resurrecting Prehistoric Predators: The Controversial Quest to Bring Back Dire Wolves
In the cutting-edge world of genetic research, a groundbreaking scientific endeavor has sparked intense debate within the scientific community. Colossal Biosciences, a pioneering biotechnology company, claims to have achieved the seemingly impossible: de-extinction of the legendary dire wolf, a prehistoric predator that once roamed the North American continent thousands of years ago.Unraveling the Mysteries of Prehistoric Genetic Resurrection
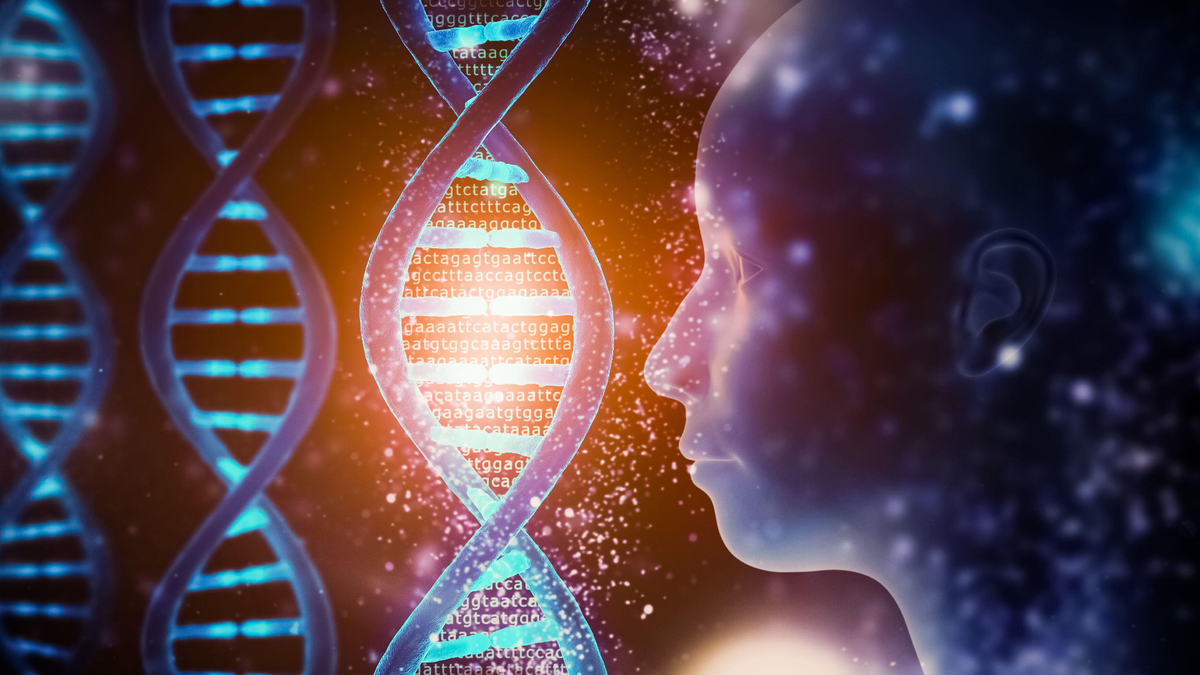
The Science Behind De-Extinction
The realm of genetic engineering has entered an unprecedented era of possibility, where scientists are pushing the boundaries of biological reconstruction. Colossal Biosciences has positioned itself at the forefront of this revolutionary field, utilizing advanced genomic technologies to potentially resurrect extinct species. The dire wolf project represents a monumental challenge, requiring intricate genetic mapping, sophisticated DNA reconstruction, and complex biological engineering techniques. Researchers must navigate an incredibly complex landscape of genetic information, piecing together fragmented DNA sequences from prehistoric remains. The process involves extracting genetic material from well-preserved specimens, analyzing molecular structures, and developing sophisticated computational models that can potentially recreate extinct genetic blueprints. This approach demands an unprecedented level of scientific precision and technological innovation.Genetic Challenges and Technological Limitations
The resurrection of extinct species presents numerous scientific and ethical challenges that extend far beyond simple genetic reconstruction. Dire wolves, which disappeared approximately 13,000 years ago, represent a particularly complex case study in de-extinction research. The genetic material available is often degraded, fragmented, and requires extensive computational analysis to reconstruct potential genomic sequences. Skeptical scientists argue that the resources invested in such speculative projects could be more effectively utilized in contemporary conservation efforts. The immense technological and financial investments required for de-extinction research potentially divert critical funding and attention from protecting existing endangered species and their habitats.Ecological and Ethical Implications
The potential reintroduction of an extinct predator like the dire wolf raises profound ecological questions. Modern ecosystems have dramatically transformed since the species' extinction, and reintroducing such a significant predator could create unpredictable and potentially destabilizing environmental consequences. Ethical considerations surrounding genetic resurrection remain complex and multifaceted. Scientists must grapple with fundamental questions about the moral implications of recreating extinct species, balancing scientific curiosity with responsible ecological stewardship. The potential risks of introducing a prehistoric predator into contemporary environments cannot be understated.Scientific Community's Response
The scientific community remains deeply divided regarding Colossal Biosciences' ambitious project. While some researchers view the initiative as a groundbreaking demonstration of technological potential, others perceive it as a potentially dangerous and misguided endeavor that could divert critical resources from more pressing conservation priorities. Prominent paleontologists and conservation biologists have expressed significant reservations about the practical feasibility and potential ecological ramifications of reintroducing an extinct predator. The complex interplay between genetic reconstruction, ecological systems, and ethical considerations demands rigorous scientific scrutiny and comprehensive interdisciplinary dialogue.Future of Genetic Research and Conservation
The dire wolf de-extinction project represents more than a singular scientific initiative; it symbolizes a broader exploration of genetic possibilities and technological boundaries. As scientific understanding continues to evolve, researchers must carefully navigate the delicate balance between technological innovation and responsible ecological management. The ongoing debate surrounding this project highlights the critical importance of maintaining robust scientific discourse, encouraging transparent research methodologies, and prioritizing comprehensive ecological understanding over sensationalized technological achievements.RELATED NEWS
Science

Breaking Barriers: How Science Journalists Are Transforming Academic Communication at Johns Hopkins
2025-04-16 14:53:00
Science

Mushroom Mystery: How a Citizen Science App Became a Key Player in a Deadly Dinner Party Investigation
2025-05-02 04:12:44