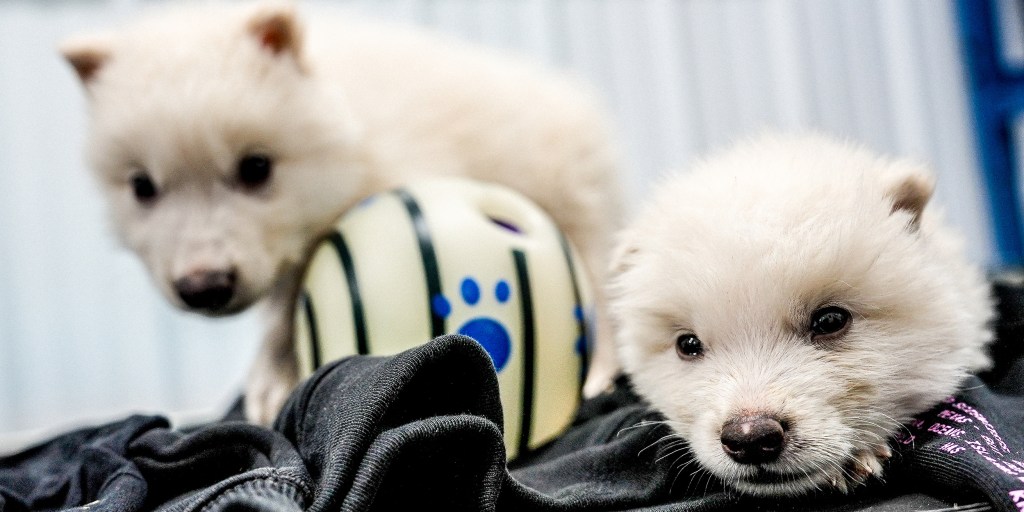
White Wolves Rising: Genetic Breakthrough Resurrects Ancient Predator's Legacy
Science
2025-04-08 03:36:09Content

Hold Your Horses: Scientists Warn Against Premature Excitement
When news breaks about potentially resurrecting an extinct species, caution is the watchword. Vincent Lynch, a biologist from the University of Buffalo, offers a critical perspective that tempers the enthusiasm surrounding such scientific breakthroughs.
"Don't mistake surface-level reconstruction for true revival," Lynch emphasizes. While recent research might create a convincing exterior resemblance of an extinct species, it falls far short of genuinely bringing a lost creature back to life. The visual similarity, he argues, is merely a superficial imitation that doesn't capture the complex biological essence of the original organism.
Lynch's insights serve as a crucial reminder that scientific advancement requires more than just recreating external appearances. True resurrection demands a profound understanding of genetic complexity, ecological interactions, and the intricate biological systems that define a species.
As researchers continue to push the boundaries of genetic science, his cautionary note encourages a measured and realistic approach to understanding the potential and limitations of species reconstruction.
Resurrecting Prehistoric Giants: The Controversial Science of De-Extinction
In the cutting-edge realm of genetic research, scientists are pushing the boundaries of biological possibility, exploring the extraordinary potential to breathe life into species long vanished from our planet. The quest to resurrect extinct creatures represents a fascinating intersection of advanced technology, evolutionary biology, and ethical scientific exploration.Unraveling Nature's Most Ambitious Genetic Reconstruction Project
The Genetic Resurrection Frontier
Modern genetic engineering has opened unprecedented pathways for scientific innovation, challenging our fundamental understanding of biological limitations. Researchers are now delving into complex methodologies that could potentially resurrect extinct species, transforming what was once considered impossible into a tangible scientific endeavor. The process involves intricate DNA reconstruction, advanced molecular techniques, and sophisticated computational modeling that allows scientists to piece together genetic blueprints of long-disappeared organisms. Cutting-edge laboratories are employing revolutionary CRISPR gene-editing technologies to meticulously reconstruct genetic sequences, creating potential pathways for species revival. These groundbreaking techniques involve extracting fragmented genetic material from preserved specimens, analyzing molecular structures, and strategically reconstructing chromosomal configurations that could theoretically resurrect extinct creatures.Challenges of Genetic Reconstruction
The scientific community remains deeply divided about the ethical and practical implications of de-extinction efforts. While technological capabilities continue expanding, significant challenges persist in recreating entire ecological systems and understanding the complex interactions between resurrected species and contemporary environments. Biological constraints present formidable obstacles. Genetic degradation over millennia means that recovered DNA fragments are often incomplete, requiring sophisticated computational algorithms and genetic interpolation techniques to fill critical informational gaps. Moreover, even perfectly reconstructed genetic sequences do not guarantee successful organism regeneration, as epigenetic factors and environmental interactions play crucial roles in biological development.Evolutionary and Ecological Implications
Reintroducing extinct species could dramatically reshape existing ecological landscapes, potentially disrupting delicate environmental balances. Scientists must carefully consider potential cascading effects on contemporary ecosystems, understanding that resurrected organisms would interact with environments fundamentally different from their original habitats. Paleontologists and genetic researchers collaborate extensively to model potential scenarios, utilizing advanced simulation technologies to predict potential ecological outcomes. These interdisciplinary efforts aim to comprehensively understand the complex ramifications of reintroducing prehistoric species into modern environments.Technological Breakthroughs and Ethical Considerations
The scientific community continues wrestling with profound ethical questions surrounding genetic resurrection. While technological capabilities expand exponentially, critical philosophical debates emerge regarding humanity's role in manipulating evolutionary processes and potentially reversing extinction events. Sophisticated genetic mapping techniques now allow researchers to reconstruct increasingly complex genetic structures, offering tantalizing glimpses into potential resurrection methodologies. However, these advancements simultaneously raise complex moral considerations about scientific intervention in natural evolutionary processes.Future Perspectives on De-Extinction
As technological capabilities continue evolving, the potential for genetic resurrection becomes increasingly sophisticated. Researchers remain cautiously optimistic about future breakthroughs, recognizing that each successful reconstruction represents a monumental scientific achievement with far-reaching implications for our understanding of biological systems. Interdisciplinary collaboration between geneticists, paleontologists, ecologists, and computational biologists will be crucial in navigating the complex landscape of species resurrection. The journey toward understanding and potentially recreating extinct organisms represents one of the most exciting frontiers in contemporary scientific research.RELATED NEWS
Science

Science Storytellers Unite: Gene Pool Media Unveils Groundbreaking Podcast Network
2025-04-25 10:01:33
Science

Calling Young Animal Lovers: Michigan's 4-H Summer Camp Registration Launches Soon!
2025-03-18 15:26:07
Science

Breaking Barriers: Young Women Unleash Tech Potential at Denver's STEM Spectacular
2025-03-08 06:15:00