Alarm Bells Ring: Unstoppable Bacterial Menace Sweeps Through Malaysian Hospitals
Health
2025-04-07 08:27:04Content
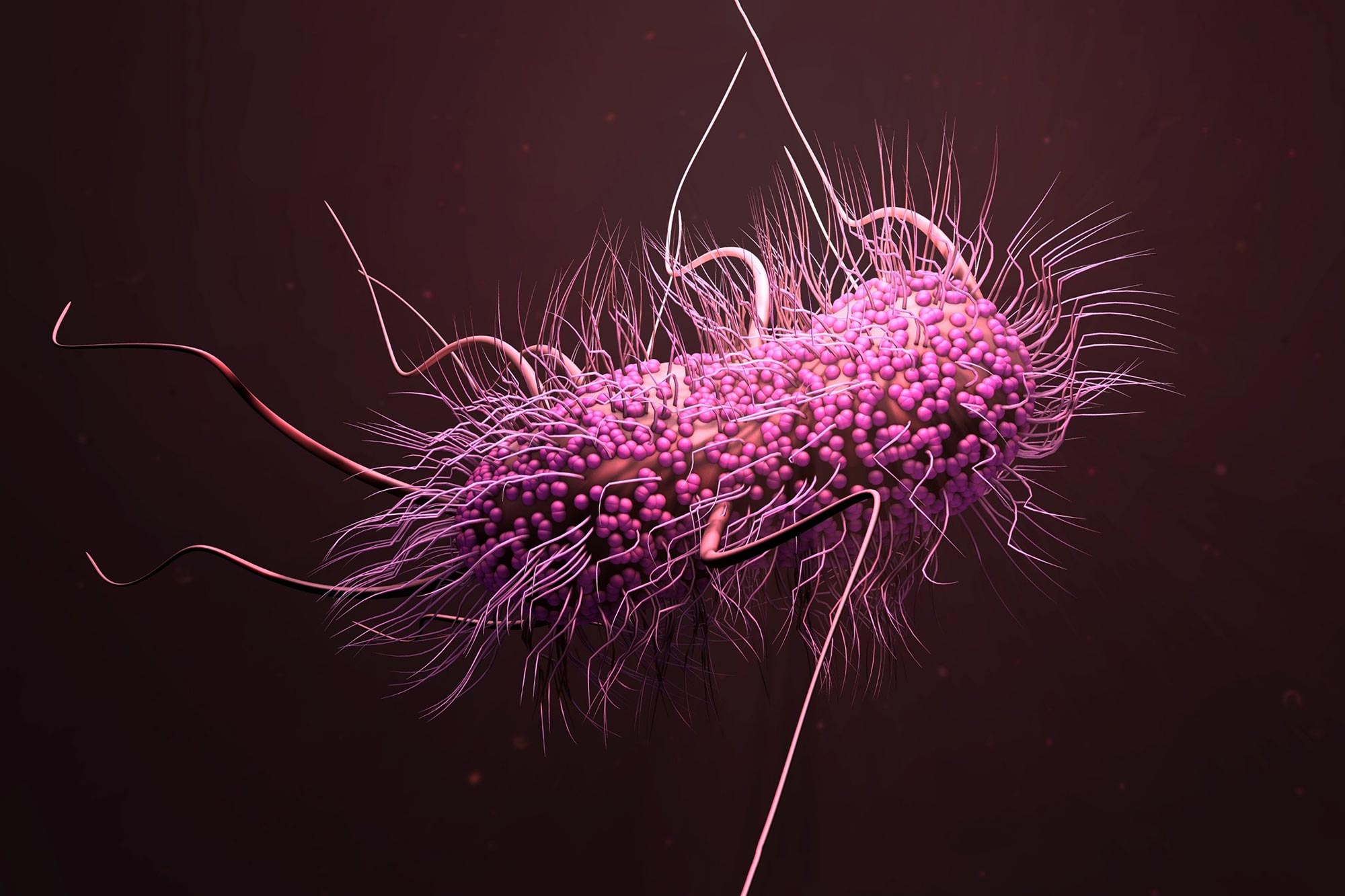
A dangerous antibiotic-resistant bacterial strain is raising global health alarms after emerging in a Malaysian hospital. The highly virulent Acinetobacter baumannii "superbug" represents a critical threat due to its remarkable resistance to multiple key antibiotics and the limited surveillance capabilities in low-income regions.
This emerging bacterial strain highlights the growing challenge of antimicrobial resistance, which could potentially compromise medical treatments and patient safety. The Malaysian hospital outbreak serves as a stark reminder of how quickly drug-resistant pathogens can spread in healthcare settings, particularly in areas with limited medical infrastructure.
Researchers are particularly concerned about the strain's ability to survive standard antibiotic treatments, making infections increasingly difficult to control. The lack of comprehensive monitoring in developing countries further compounds the risk, potentially allowing such resistant bacteria to proliferate undetected.
The discovery underscores the urgent need for enhanced global health monitoring, robust infection control protocols, and continued research into developing more effective antimicrobial strategies to combat these evolving bacterial threats.
Silent Killer Emerges: The Antibiotic-Resistant Menace Threatening Global Health
In the shadowy corridors of modern medical challenges, a microscopic threat is silently evolving, challenging our most fundamental healthcare defenses. The emergence of drug-resistant bacterial strains represents a critical turning point in global public health, where traditional medical interventions are being systematically undermined by nature's most adaptable organisms.When Superbugs Outsmart Modern Medicine: A Critical Global Health Warning
The Microbial Warfare: Understanding Antibiotic Resistance
The battle between human medical science and bacterial evolution has reached a critical juncture. Antibiotic-resistant bacteria represent a sophisticated survival mechanism that threatens to unravel decades of medical progress. These microorganisms have developed intricate molecular strategies to neutralize pharmaceutical interventions, creating a complex ecological arms race within human biological systems. Researchers worldwide are increasingly alarmed by the rapid genetic mutations occurring in bacterial populations. These transformations enable pathogens to develop sophisticated defense mechanisms, rendering traditional antibiotics ineffective. The genetic plasticity of bacteria allows them to share resistance mechanisms through horizontal gene transfer, creating a networked defense system that continuously adapts and evolves.Malaysian Hospital: Ground Zero for Emerging Bacterial Threat
The recent identification of a highly virulent bacterial strain in a Malaysian medical facility has sent shockwaves through the global scientific community. This particular strain of Acinetobacter baumannii demonstrates unprecedented resistance to multiple antibiotic classes, representing a significant escalation in microbial threat potential. Medical epidemiologists are particularly concerned about the strain's ability to survive in challenging hospital environments. Its robust genetic structure enables prolonged survival on surfaces, medical equipment, and within complex healthcare ecosystems. This characteristic exponentially increases transmission risks, potentially transforming hospitals from healing spaces into potential infection vectors.Global Health Implications and Systemic Vulnerabilities
The emergence of such drug-resistant bacterial strains exposes critical vulnerabilities in global healthcare infrastructure. Low-income regions, characterized by limited surveillance and restricted medical resources, become potential breeding grounds for these microbial threats. The lack of comprehensive monitoring systems means these dangerous bacterial mutations can proliferate undetected. International health organizations are increasingly advocating for enhanced global cooperation in tracking and managing antibiotic-resistant organisms. The interconnected nature of modern global travel means that a localized bacterial threat can rapidly transform into an international public health emergency. Sophisticated genomic tracking and real-time molecular surveillance have become essential tools in understanding and mitigating these emerging risks.Scientific Strategies: Combating the Superbug Phenomenon
Cutting-edge research is exploring multifaceted approaches to address the superbug challenge. Advanced molecular techniques, including CRISPR gene editing and bacteriophage therapies, represent promising frontiers in developing innovative bacterial control strategies. Scientists are essentially reimagining our approach from traditional antibiotic treatments to more nuanced, targeted interventions. Interdisciplinary collaboration between microbiologists, geneticists, and computational researchers is accelerating our understanding of bacterial adaptation mechanisms. Machine learning algorithms are now being deployed to predict potential mutation pathways, allowing preemptive medical strategies that could potentially neutralize bacterial resistance before it fully manifests.Societal Preparedness and Future Outlook
The ongoing battle against antibiotic-resistant bacteria demands a holistic, globally coordinated response. Public health education, responsible antibiotic usage, and continuous scientific innovation will be crucial in mitigating these emerging threats. As bacterial populations continue to evolve, human medical science must maintain an equally dynamic and adaptive approach. The Malaysian hospital's discovery serves as a critical warning, highlighting the urgent need for sustained investment in medical research, enhanced global surveillance systems, and proactive public health strategies. Our collective future depends on our ability to understand, predict, and effectively respond to these microscopic evolutionary challenges.RELATED NEWS
Health

AI Revolution: How One Harvard Student Plans to Supercharge Public Health
2025-03-25 20:49:48
Health

Speed, Strategy, and Survival: Inside NASCAR's High-Octane Atlanta Showdown
2025-02-22 12:03:20