Danger Zones: CDC Sounds Alarm on Rapidly Spreading Dengue Threat
Health
2025-03-19 12:46:34Content
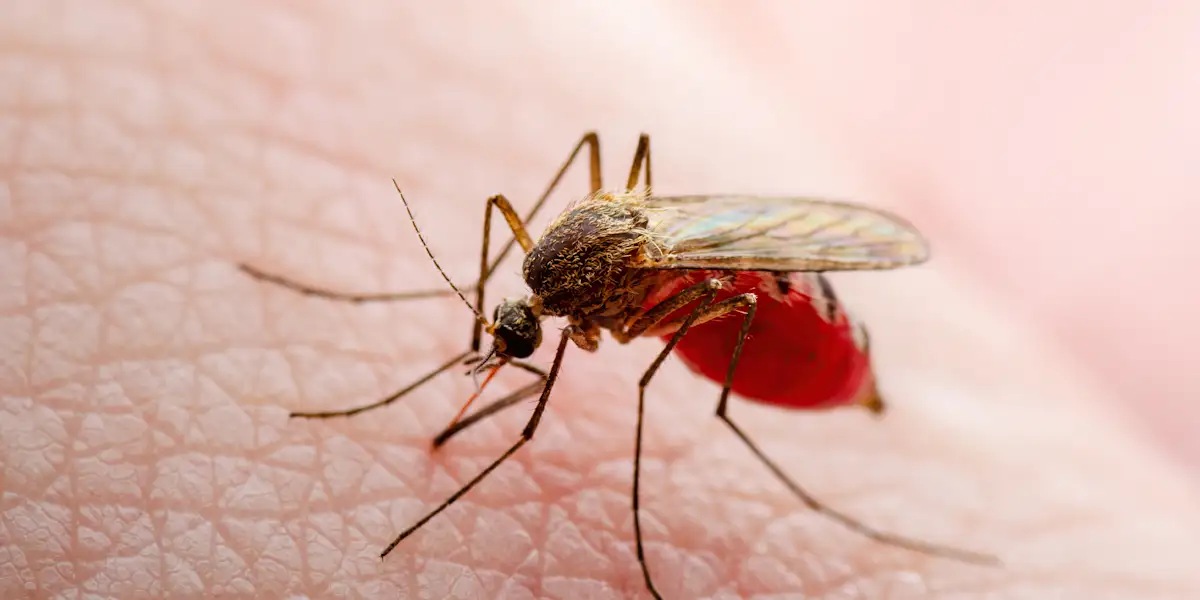
Dengue Virus: A Growing Threat in US Regions
As summer temperatures rise, health experts are sounding the alarm about persistent dengue virus transmission in select parts of the United States. This mosquito-borne illness, once considered primarily a tropical disease, is increasingly making its presence known in American communities.
What makes dengue particularly concerning is its potential for rapid spread and serious health complications. The virus, transmitted through the bite of infected Aedes mosquitoes, can cause a range of symptoms from mild flu-like conditions to severe, potentially life-threatening complications.
Key Signs to Watch For:
• High fever (104°F or higher)
• Severe headaches
• Pain behind the eyes
• Muscle and joint pain
• Unusual skin rashes
• Mild bleeding from nose or gums
Regions at Higher Risk:
Southeastern states like Florida and Texas, along with parts of Hawaii, are experiencing the most significant dengue activity. Residents in these areas should be especially vigilant about mosquito prevention and personal protection.
Prevention Tips:
• Use EPA-registered insect repellents
• Wear long-sleeved clothing
• Eliminate standing water around homes
• Use window and door screens
• Consider mosquito nets in high-risk areas
If you experience persistent symptoms, seek medical attention promptly. Early detection and proper medical care can significantly improve outcomes for dengue patients.
Silent Threat: The Escalating Dengue Crisis Sweeping Across American Territories
In the intricate landscape of emerging health challenges, a microscopic predator is silently transforming public health dynamics across select regions of the United States. Dengue fever, once considered a distant tropical concern, has now emerged as a formidable adversary, threatening communities with its complex transmission patterns and potentially severe health implications.Unraveling the Hidden Epidemic: What Every American Needs to Know
Understanding Dengue's Geographical Footprint
Dengue virus represents a complex epidemiological puzzle that transcends traditional geographical boundaries. Recent surveillance data reveals alarming transmission rates in specific U.S. territories, particularly in regions with subtropical and tropical climatic conditions. Puerto Rico, Florida, and Hawaii have emerged as critical hotspots, experiencing unprecedented viral circulation that challenges conventional public health strategies. The virus's transmission dynamics are intricately linked to environmental factors, mosquito population densities, and human mobility patterns. Climate change has significantly expanded mosquito habitats, creating unprecedented opportunities for viral spread beyond traditional endemic zones.Decoding Transmission Mechanisms
Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes serve as primary viral vectors, transforming seemingly innocuous urban and suburban landscapes into potential transmission zones. These resilient insects thrive in human-modified environments, exploiting standing water sources, urban infrastructure, and microclimatic conditions to proliferate rapidly. Transmission occurs through complex interactions between infected mosquitoes, human hosts, and environmental conditions. Unlike many viral diseases, dengue's transmission requires precise ecological synchronization, making prevention a multifaceted challenge for public health professionals.Recognizing Symptomatic Manifestations
Dengue's clinical presentation ranges from asymptomatic infections to potentially life-threatening hemorrhagic conditions. Initial symptoms often mimic common viral infections, including high fever, severe headaches, muscle and joint pain, and characteristic skin rashes. Medical professionals emphasize the critical importance of early detection and comprehensive diagnostic protocols. Advanced molecular testing techniques have revolutionized diagnostic capabilities, enabling more precise viral strain identification and targeted intervention strategies.Emerging Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
Contemporary public health approaches demand integrated, multidisciplinary strategies combining epidemiological surveillance, vector control, community education, and advanced medical interventions. Innovative mosquito control technologies, including genetic modification techniques and advanced biological control methods, represent promising frontiers in combating viral transmission. Community-based prevention programs have demonstrated remarkable efficacy in reducing transmission risks. These initiatives focus on eliminating mosquito breeding environments, promoting personal protection measures, and enhancing public awareness about viral transmission mechanisms.Technological Innovations in Dengue Management
Cutting-edge research is revolutionizing dengue management through advanced predictive modeling, real-time surveillance systems, and targeted intervention protocols. Machine learning algorithms now enable more accurate transmission risk assessments, empowering public health authorities to implement proactive containment strategies. Emerging vaccine technologies and targeted therapeutic interventions offer hope for more comprehensive disease management. Researchers are exploring novel approaches that could potentially disrupt viral transmission cycles and mitigate long-term health consequences.Global and Local Implications
The expanding dengue landscape underscores the interconnected nature of modern public health challenges. As global climate patterns shift and human mobility increases, viral transmission dynamics become increasingly complex and unpredictable. Local and federal health authorities must continuously adapt their strategies, leveraging interdisciplinary research, advanced technological solutions, and community-centered approaches to effectively address this evolving health threat.RELATED NEWS
Health

Wellness Revolution: Discover Your Path to Optimal Health at Community Expo
2025-05-06 18:41:17
Health

Mental Health in Crisis: Jordan Peterson Exposes the Hidden Barriers to Care
2025-02-18 20:23:54






