The Silent Corrosion: How Road Salt Turns Your Car into a Rust Bucket and Threatens Ecosystems
Environment
2025-02-16 15:22:14Content
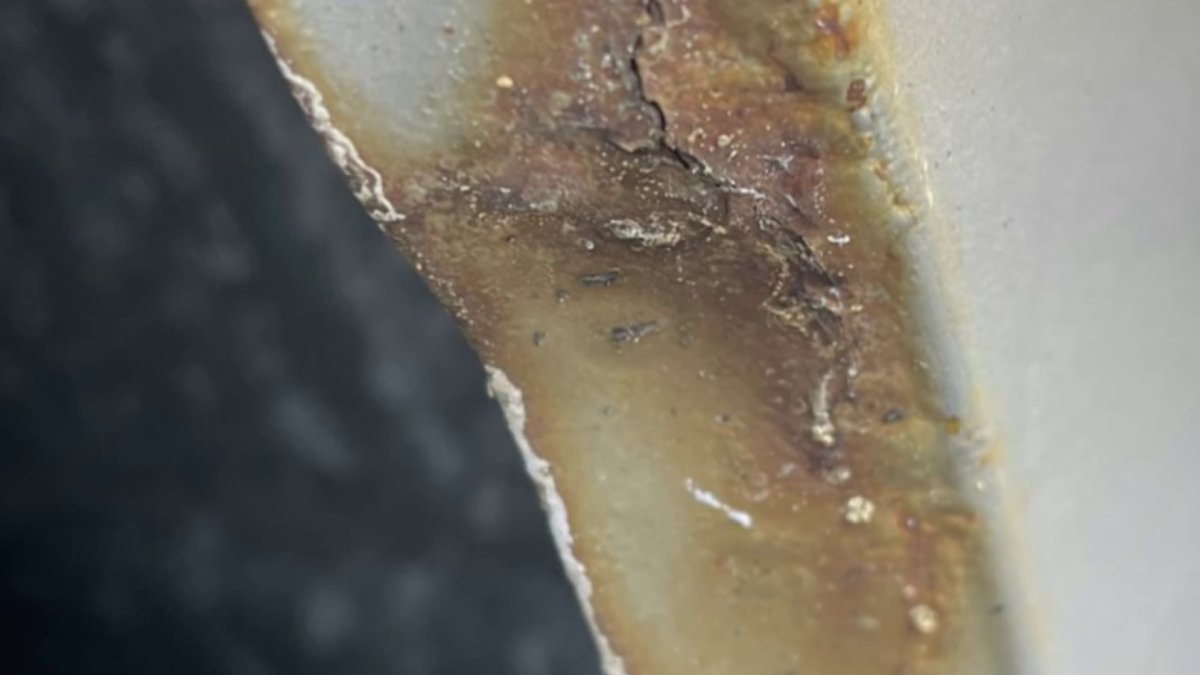
When winter storms blanket our roads with snow and ice, road salt becomes a critical tool for keeping highways safe. But Storm Team4 Meteorologist Ryan Miller warns that this seemingly helpful solution comes with significant environmental consequences.
Road salt, while effective at melting ice and improving driving conditions, can cause serious damage to our ecosystem and infrastructure. As the salt dissolves, it doesn't just disappear—it seeps into soil, waterways, and groundwater, creating a cascade of environmental challenges.
The most immediate impact is on local vegetation. High salt concentrations can disrupt plant root systems, making it difficult for trees, grass, and other greenery to absorb essential nutrients. Moreover, the salt runoff can increase water salinity, harming aquatic life and disrupting delicate environmental balances.
Perhaps less obvious is the accelerated corrosion of vehicles and infrastructure. Salt dramatically speeds up the rusting process, causing premature deterioration of car undercarriages, bridges, and roadside structures. What might seem like a quick fix for winter driving can lead to long-term economic costs through increased maintenance and replacement expenses.
Miller emphasizes the importance of using road salt judiciously and exploring more environmentally friendly de-icing alternatives that can minimize ecological impact while maintaining road safety.
Environmental Impact Unveiled: The Hidden Dangers of Road Salt During Winter Storms
Winter's icy grip transforms landscapes into treacherous terrains, compelling municipalities and road maintenance crews to deploy salt as a primary defense against hazardous road conditions. However, beneath this seemingly innocuous solution lies a complex environmental challenge that demands urgent attention and innovative alternatives.Unraveling the Ecological Consequences of Winter Road Treatment Strategies
The Chemical Composition of Road Salt and Its Environmental Footprint
Road salt, predominantly composed of sodium chloride, represents a seemingly straightforward solution to winter road safety. Yet, its environmental ramifications extend far beyond immediate ice mitigation. When applied extensively, these chemical compounds penetrate soil ecosystems, disrupting delicate microbial balances and compromising vegetation health. Researchers have documented significant alterations in soil chemistry, with salt concentrations causing profound shifts in nutrient availability and microbial community structures. The infiltration of road salt into groundwater systems presents another critical concern. As these mineral-laden solutions percolate through geological strata, they fundamentally transform aquatic environments. Freshwater ecosystems experience dramatic salinity increases, challenging the survival mechanisms of indigenous species and potentially triggering cascading ecological disruptions.Corrosion and Infrastructure Degradation: The Hidden Economic Toll
Beyond environmental consequences, road salt accelerates infrastructure deterioration through aggressive corrosion mechanisms. Metallic structures, including bridges, guardrails, and vehicular components, face accelerated oxidation processes when repeatedly exposed to salt-laden environments. The electrochemical interactions between salt molecules and metal surfaces create microscopic degradation pathways, progressively compromising structural integrity. Transportation departments nationwide invest billions annually in infrastructure maintenance, with a significant portion attributable to salt-induced corrosion. The economic implications extend beyond immediate repair costs, encompassing long-term structural vulnerabilities and potential safety risks associated with premature material degradation.Innovative Alternatives and Sustainable De-icing Technologies
Emerging research focuses on developing environmentally conscious de-icing strategies that minimize ecological disruption. Cutting-edge technologies explore biodegradable compounds, organic salt mixtures, and advanced thermal management techniques. Pioneering municipalities have begun experimenting with brine solutions enhanced with organic additives, demonstrating promising results in reducing environmental impact while maintaining road safety standards. These innovative approaches represent a paradigm shift in winter road management, prioritizing ecological preservation alongside transportation infrastructure maintenance. By integrating advanced material sciences with environmental consciousness, researchers aim to develop holistic solutions that balance human safety with ecosystem protection.Physiological Impacts on Local Wildlife and Vegetation
The pervasive use of road salt creates intricate challenges for local flora and fauna. Wildlife populations experience significant physiological stress when exposed to elevated salt concentrations. Amphibian species, particularly sensitive to environmental changes, demonstrate reduced reproductive capabilities and compromised immune responses in salt-saturated habitats. Vegetation along roadways experiences profound transformation, with salt-tolerant species gradually displacing native plant communities. This ecological shift represents a nuanced yet significant modification of regional biodiversity, potentially triggering long-term evolutionary adaptations among local ecosystems.Global Perspectives and Regulatory Considerations
International environmental policy increasingly recognizes the complex challenges posed by road salt usage. Regulatory frameworks are evolving to incorporate more stringent guidelines, encouraging municipalities to adopt sustainable winter maintenance practices. Collaborative research initiatives between environmental scientists, transportation experts, and policymakers aim to develop comprehensive strategies that balance safety requirements with ecological preservation. The ongoing dialogue surrounding road salt usage represents a microcosm of broader environmental management challenges, highlighting the intricate relationships between human infrastructure and natural systems.RELATED NEWS
Environment

Environmental Watchdogs Axed: E.P.A. Shutters Justice Divisions in Controversial Move
2025-03-12 03:35:16
Environment

Digital Powerhouses: Are Data Centers Saving the Economy or Killing the Planet?
2025-04-15 01:59:00






